Creating a table is the core of the database design. Data is stored in tables, and the table structure with internal relations allows us to organize that data effectively. It is impossible to work with databases without creating and configuring tables, and it is one of the fundamental skills for all database professionals.
There are standard methods of creating tables and tips that help us to do it faster and ensure accuracy. This article aims to review these methods and tips on Microsoft’s SQL Server – the data platform and one of the world’s most popular database management systems.
Contents
- The basics of creating database tables
- The CREATE TABLE statement
- CREATE TABLE with a primary key
- CREATE TABLE with a foreign key
- CREATE TABLE from another table
- CREATE TABLE if it does not exist
- CREATE a temp table
- The advantages of using GUI tools for creating tables
- Conclusion
The basics of creating database tables
The database table is a structure that contains data organized by rows and columns. Tables have descriptive names. Table columns also have specific names. Besides, each column is assigned the data type that defines which values that column can store.
SQL Server provides the following options for creating tables:
- The CREATE TABLE command: This is the standard method used to create a SQL Server table. Here we can specify columns, data types, set constraints, and define other table properties. Besides, it allows the developers to save the script and reuse it whenever needed, even automatically.
- The SELECT AS/SELECT INTO command: This method creates a new table from the existing one based on the SELECT query result set. The resulting table inherits the structure of the “source” table, whether or not it contains any records. This method provides a convenient way to generate a new table with the same structure as the original one.
- GUI-based software tools (SSMS or third-party solutions): Graphical user interfaces are favored by both database experts and regular users as they streamline all processes and eliminate errors caused by manual coding. SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is the default solution provided by Microsoft.
This article will demonstrate how to create new tables in SQL Server with dedicated scripts. However, we’ll also utilize GUI tools to illustrate our work – we appeal to dbForge Studio for SQL Server, a more powerful and robust alternative to SSMS that allows us to design database tables in several clicks.
The CREATE TABLE statement
Syntax
The basic syntax we use to create a new table in SQL Server is:
CREATE TABLE [database_name.][schema_name.]table_name (
column_name1 data_type [NULL | NOT NULL],
column_name2 data_type [NULL | NOT NULL],
column_name3 data_type [NULL | NOT NULL],
...,
);Note the following parameters:
database_name and schema_name – optional parameters that define respectively the names of the database and the database schema where you are creating the new table. If they aren’t specified explicitly, the query will be executed against the current database and the default schema of that database.
table_name – the name of the table you are creating. The maximum length of the table name is 128 characters (except for the local temporary tables – we’ll review them further in this article). It is recommended to use descriptive names to manage tables easier.
column_name – the name of the column in the table. Most tables contain multiple columns, and we separate column names in the CREATE TABLE script by commas.
data_type – the data type for each column to indicate which values that particular column will store.
NOT NULL – the optional parameter that specifies that the column cannot contain NULL values. If it is not set, the column allows having NULL values.
The CREATE TABLE statement can be significantly more intricate and incorporate a wider array of parameters, whereas this syntax represents the simplest variant. But for now, let us see how the basic syntax works.
Have you ever considered using a table designer tool to create new SQL tables or edit table data in the grid visually? If not, it’s about time to give it a try!
Example
Assume we want to create a table in a shop database with information about regular customers.
CREATE TABLE sales.customers (
customer_id INT IDENTITY (1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
phone VARCHAR (25),
email VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
street VARCHAR (255),
city VARCHAR (50),
state VARCHAR (25),
zip_code VARCHAR (5)
);This is what it looks like in SSMS and dbForge Studio for SQL Server, respectively.
Check the list of the best free SQL database software to try in 2025.
That’s how we have created a new table in the existing SQL Server database.
CREATE TABLE with a primary key
The primary key is a constraint that identifies each table record uniquely. It is not mandatory, but it is present in most tables. Most likely, we’ll need it too.
Syntax
The primary key has the following characteristics:
- Contains unique values only
- Can be only one on a table
- Can’t contain NULL values
- Consists of one or several columns
Thus, the basic syntax for this case is:
CREATE TABLE [database_name.][schema_name.]table_name (
column_name1 data_type NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
column_name2 data_type [NULL | NOT NULL],
column_name3 data_type [NULL | NOT NULL],
...,
);Example #1
So, to create a table in SQL Server with a primary key, we use the PRIMARY KEY keyword for the respective column after its name and data type.
CREATE TABLE production.categories (
category_id INT IDENTITY (1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
category_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL
);
Example #2
Setting a primary key is possible for any column or a combination of columns.
CREATE TABLE sales.customers (
first_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
phone VARCHAR (25) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
street VARCHAR (255),
city VARCHAR (50),
state VARCHAR (25),
zip_code VARCHAR (5),
CONSTRAINT PK_Customer PRIMARY KEY (first_name, last_name, phone, email)
);
In the above example, we create a table with a primary key that involves four columns – the first name, the last name, the phone number, and the email address. This combination will be used to identify each record in the table.
CREATE TABLE with a foreign key
The foreign key constraint is an essential element for relational databases – it creates the relation between tables by referring to the primary key set on a different table. As a result, two tables get linked together.
The table with the primary key is called the parent table, and the table with the foreign key is called the child table. The values used by the foreign key of the child table must exist in the parent table.
It is a common practice to create a table in SQL Server with a foreign key at once to relate it to another table and make the entire schema more organized.
Syntax
The basic syntax for this case is:
CREATE TABLE [database_name.][schema_name.]table_name (
column_name1 data_type NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
column_name2 data_type [NULL | NOT NULL],
column_name3 data_type [NULL | NOT NULL],
...,
FOREIGN KEY
( column_name [ ,... n ] )
REFERENCES referenced_table_name [ ( ref_column [ ,... n ] ) ]
);Here, we take the general syntax for the previous case, add a foreign key constraint, and indicate the referenced table and column.
Example
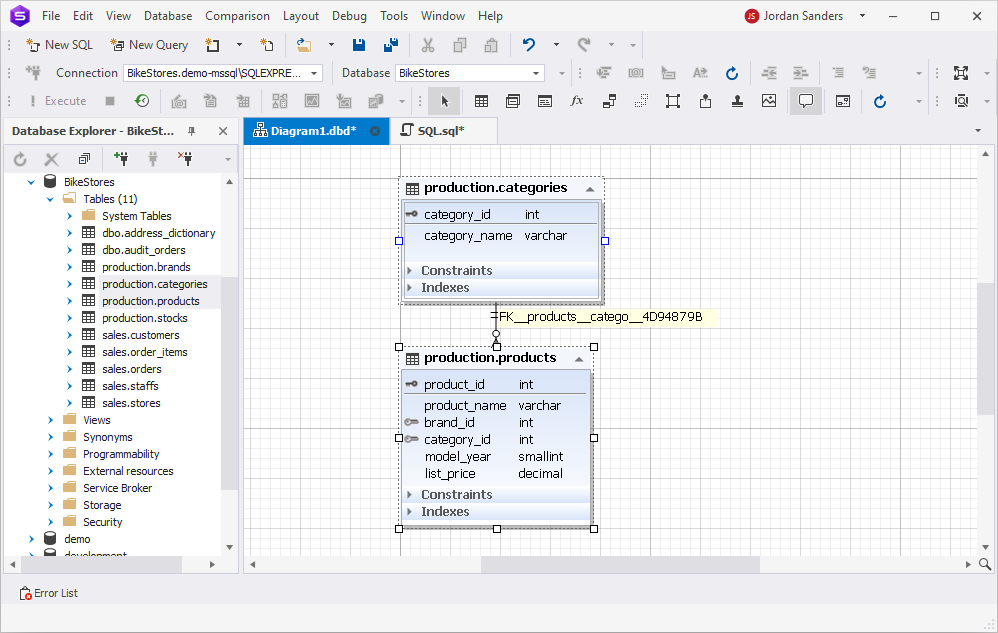
Assume we want to create a table with information about products. It will be a child table for the production.categories table, and we’ll have a foreign key on it.
CREATE TABLE production.products (
product_id INT IDENTITY (1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
product_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
brand_id INT NOT NULL,
category_id INT NOT NULL,
model_year SMALLINT NOT NULL,
list_price DECIMAL (10, 2) NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (category_id) REFERENCES production.categories (category_id)
);
This way, we create a table with a foreign key in SQL Server and relate two tables (production.products and production.categories). The product_id column is the primary key of the production.products table, and the category_id column is the foreign key referencing the category_id column in the parent production.categories table.
CREATE TABLE from another table
Syntax
Creating a new table in a database from an existing table is common. We use the SELECT…INTO statement for that. It fetches columns from an existing table and inserts them into a new table.
SELECT column1, column2, column3
INTO [external_db.][schema_name.]new_table
FROM [database_name.][schema_name.]old_table
WHERE condition;Note the WHERE clause, which can be used to specify the data you want to retrieve and save in a new table.
Example #1
Now let’s see how it works. For example, let’s create a comprehensive list of customers’ addresses.
SELECT street, city, state, zip_code
INTO address_dictionary
FROM BikeStores.sales.customers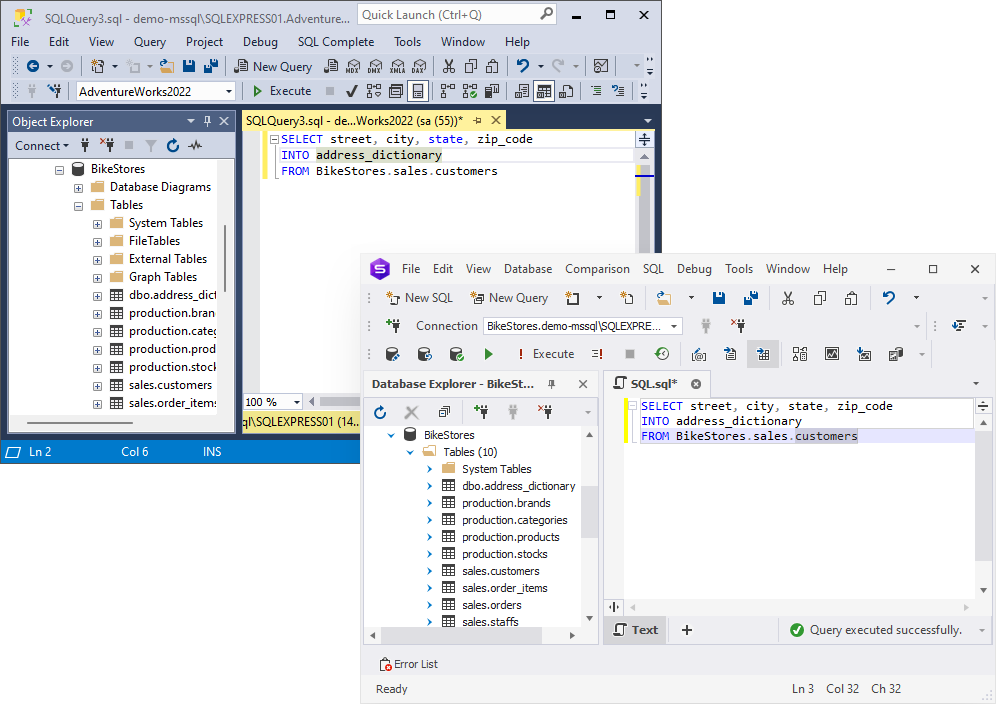
Example #2
One of the scenarios where SELECT INTO comes in handy is creating empty tables with a specific structure. For that, we take our basic syntax and add the WHERE clause with the 1 = 0 parameter:
SELECT column1, column2, column3, ...
INTO new_table
FROM old_table
WHERE 1 = 0;This parameter ensures that the query won’t copy any data from the source table. It will create an empty table with the same structure as the original one, and you can populate its columns with your data.
SELECT *
INTO audit_orders
FROM sales.orders o WHERE 1=0;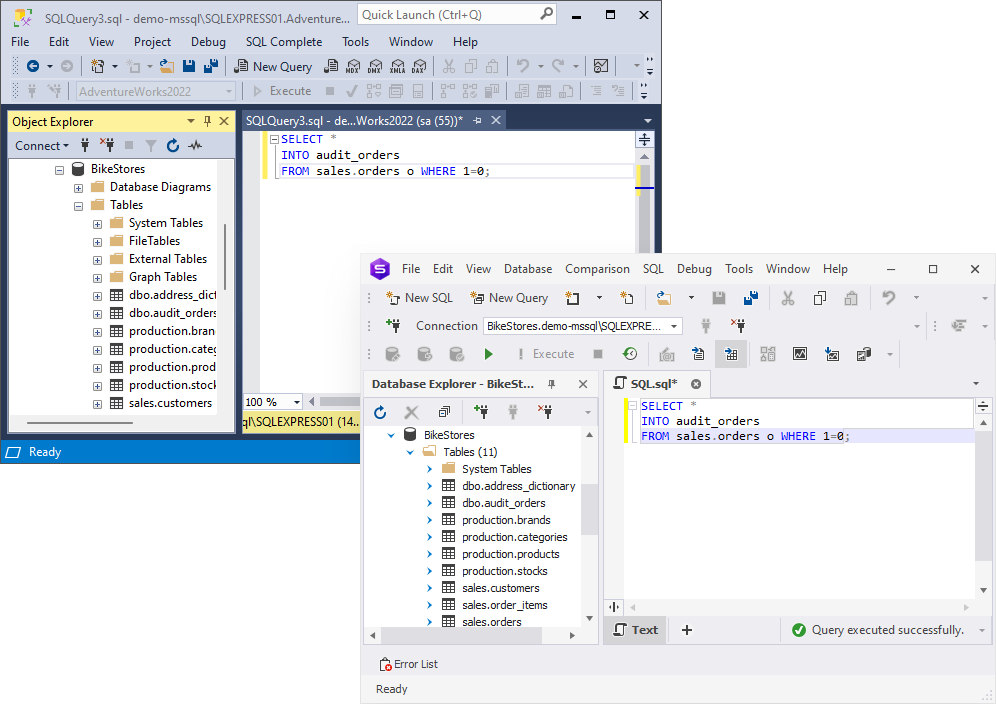
However, indexes, constraints, and triggers aren’t transferred through SELECT INTO. If you need them in a new table, you should add them separately.
CREATE TABLE if it does not exist
Before creating a new table in a database, checking whether such a table already exists would be helpful. And here the issue is: Microsoft SQL Server does not support the IF NOT EXISTS function in the CREATE TABLE queries. Should the database contain the same table, the command to create a new one with the same name will fail.
Syntax
Is there some alternative to CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS in SQL Server? The recommended solution is the OBJECT_ID() function.
IF OBJECT_ID(N'table_name', N'U') IS NULL
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column_name1 data_type [NULL | NOT NULL],
column_name2 data_type [NULL | NOT NULL],
column_name3 data_type [NULL | NOT NULL],
...,
);Example
In this example, we specify our object – the user-defined table. If this object does not exist in the database, the function returns NULL, which is the condition of creating a new table.
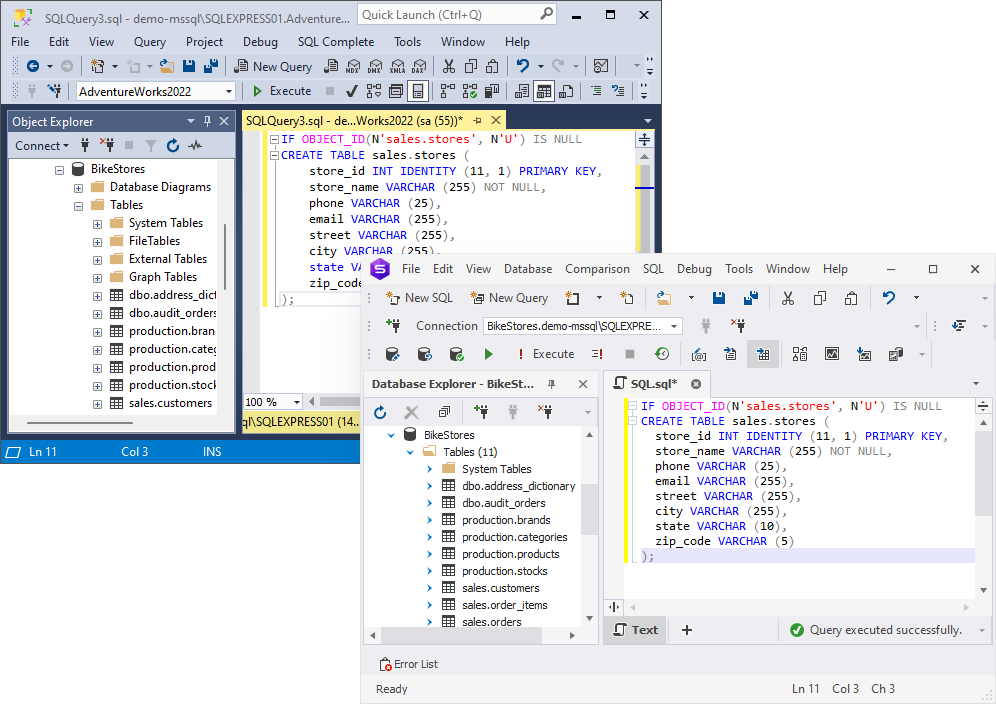
Assume we want a new table called sales.stores. Let’s check if it exists before executing the query to create it.
IF OBJECT_ID(N'sales.stores', N'U') IS NULL
CREATE TABLE sales.stores (
store_id INT IDENTITY (11, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
store_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
phone VARCHAR (25),
email VARCHAR (255),
street VARCHAR (255),
city VARCHAR (255),
state VARCHAR (10),
zip_code VARCHAR (5)
);
Thus, the CREATE TABLE command is successful, and we have a new sales.stores table in our database.
CREATE a temp table
In SQL Server, a temporary (temp) table is a table with some data portion extracted from the regular table and not stored in the memory. While it is possible to use and reuse this table during a particular session, it will be deleted when that session ends or the database connection is terminated.
Temp tables are convenient to work with if we regularly deal with some records kept in the database. We can retrieve that data, process it as needed, and turn it into a temporary table. The table is stored in the tempdb system database, and we can operate it the same way as regular tables. Temp tables are significantly faster in loading data.
Syntax
To create a temp table on SQL Server, we can use the SELECT…INTO command – it is the simplest approach:
SELECT column1, column2, column3, ...
INTO #new_table
FROM old_table
WHERE condition;Important: The temp table name always starts with the hash symbol (#), and the maximum name length is 116 characters.
Example #1
Let’s create a temp table based on our syntax, listing orders placed by customers whose State is indicated as NY.
SELECT
o.order_id,
o.customer_id,
o.order_status,
o.order_date,
o.required_date,
o.shipped_date,
o.store_id,
o.staff_id
INTO #temp_sales_orders
FROM sales.orders o
JOIN sales.customers c ON o.customer_id = c.customer_id
WHERE c.state = 'NY';
Example #2
Another way to create a temp table in SQL Server is by using the CREATE TABLE statement. It works in the same way as in the earlier examples of creating regular tables. You only need to begin the table name with the hash symbol (#).
CREATE TABLE #temp_sales_orders (
order_id INT IDENTITY (1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
customer_id INT,
order_status TINYINT NOT NULL,
order_date DATE NOT NULL,
required_date DATE NOT NULL,
shipped_date DATE,
store_id INT NOT NULL,
staff_id INT NOT NULL
);
Then, we insert records into this table and work with it as required. When the session is over, the table will be automatically deleted.
Example #3
In some work scenarios, we need to create a temporary table in SQL Server and make it accessible to other users. The solution is a global temporary table visible to all users and their sessions.
To create a global temporary table, we use the CREATE TABLE command and mark the table name with two hash symbols: ##table_name.
CREATE TABLE ##temp_2024_sales_orders (
order_id INT IDENTITY (1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
customer_id INT,
order_status TINYINT NOT NULL,
order_date DATE NOT NULL,
required_date DATE NOT NULL,
shipped_date DATE,
store_id INT NOT NULL,
staff_id INT NOT NULL
);
Global temporary tables are also stored in the system tempdb database. They remain there until all users who refer to the particular temp table complete their sessions or close connections to the database.
The advantages of using GUI tools for creating tables
Table design is one of the most common tasks, and cutting-edge GUI tools help database specialists resolve such tasks quickly and efficiently.
To support this article, we used dbForge Studio as it is one of the most popular and powerful IDEs for database-related jobs in SQL Server. It simplifies the table design significantly by transferring the work into the visual interface, though it provides a powerful SQL Editor to write SQL queries and execute them against the database directly. For instance, you can use any standard commands like ALTER TABLE to add multiple columns to the existing table and modify the tables in other ways or visit the website to learn how to list all tables in SQL.
Table Designer allows creating and modifying tables visually. It has all the options to define table columns, data types, constraints, relationships, and other properties.
Instead of writing complex SQL scripts manually, you can complete the task with several clicks. Once the table structure is defined visually, Table Designer can generate an SQL script that can be executed against the database to create that table in it, or you can save it for further reference.
dbForge Studio for SQL Server is available for a 30-day free trial, so you can explore the entire range of its capabilities and see whether it’s the best fit for your routine database development and management needs.
Tip: The CREATE TABLE command is often included in interview questions on SQL, especially for entry-level and mid-level roles. Candidates may be asked to define tables, set primary and foreign keys, or explain the difference between temporary and permanent tables. Practicing examples like those shown above can help reinforce both syntax and reasoning for interview scenarios.
Conclusion
Tables are a fundamental component of any relational database. They make it possible to both store and organize data. That’s why understanding and mastering approaches to creating tables is critical for database developers and admins. Professional expertise and the right tools help them raise their effectiveness and productivity, and this combination can’t be beaten.

