Today, about 20-40% of developer time is spent on debugging and maintenance, which is why Oracle AI is redefining SQL optimization altogether. As AI-driven automation accelerates across the Oracle ecosystem, Oracle AI Database 26ai brings machine learning, generative AI, and real-time analytics directly into the SQL engine: reducing the need for manual tuning with built-in, AI-powered automation.
This shift addresses the core performance challenges teams face every day: slow queries, complex joins, unpredictable runtimes, and hours lost chasing plan regressions. Instead of reacting after performance drops, Oracle 26ai learns from workload patterns, anticipates bottlenecks, and keeps execution stable as data and demand grow.
In the sections that follow, we break down how Oracle 26ai operates, the AI features behind its performance gains, and how other SQL AI tools accelerate SQL development.
By using Oracle 26ai, you will be able to:
- Speed up SQL development with AI-assisted workflows.
- Adjust execution plans automatically for stable performance.
- Generate optimized SQL from natural-language prompts.
- Cut time spent tuning indexes and fixing regressions.
- Reduce slowdowns across large or complex workloads.
- Let developers spend time on building real features, not fighting tooling.
- Understanding Oracle’s vision for AI-driven databases
- Why traditional SQL optimization is no longer enough
- Comparison table: Traditional vs AI-driven SQL optimization
- Core AI features enhancing SQL optimization
- AI vector search and semantic indexing
- Autonomous SQL tuning and execution plan optimization
- Generative AI for SQL code suggestions
- Predictive resource management and workload optimization
- Intelligent query diagnostics and self-healing mechanisms
- Unified AI integration for structured and unstructured data
- Practical use cases: Oracle AI in SQL optimization
- Best practices for using AI in SQL optimization
- How dbForge tools empower AI-driven SQL optimization
- Final word
- FAQ
Understanding Oracle’s vision for AI-driven databases
Oracle’s vision for an AI-driven data platform starts with a simple but powerful idea: intelligence should live inside the database, not around it. This “AI for Data” philosophy is what shapes Oracle AI Database 26ai. Instead of bolting AI on through plugins or external services, Oracle brings optimization, reasoning, and semantic understanding directly into SQL execution.
To make this possible, Oracle 26ai integrates capabilities such as:
- Machine learning–driven optimization, where models continuously learn from workload telemetry and shape execution plans in real time.
- Vector search and semantic indexing, enabling SQL to return contextually similar results rather than relying solely on exact matches.
- Agentic AI, which automates reasoning tasks and orchestrates optimization workflows directly inside the database.
This architecture marks a clear shift from traditional AI approaches. Oracle 26ai runs much of this intelligence directly in the database engine, especially in the optimizer and storage layer, reducing reliance on external ML pipelines. With AI operating where the data lives, the database reduces overhead and delivers consistently optimized performance at scale.
Example: Consider a complex analytics query that once required manual join rewrites and index tuning. In 26ai, the database automatically restructures the statement, applies vector-based filtering, and selects the optimal plan, turning developer intent into optimized execution.
Oracle strengthens this approach through partnerships with NVIDIA and the U.S. Department of Energy, ensuring high-performance AI compute sits close to enterprise data and scaling workloads smoothly across environments.
Why traditional SQL optimization is no longer enough
Traditional SQL tuning worked well when workloads were stable and environments were predictable. But today’s Oracle systems look very different. They run across hybrid clouds, support real-time analytics, and handle workloads that can spike or shift without warning. In that world, manual tuning is not enough.
Here’s why manual tuning falls short today:
- Workloads change faster than DBAs can diagnose and retune queries.
- Execution plans shift as data grows or distribution changes.
- It’s impossible to manually inspect thousands of queries running in parallel.
- Traditional hints and indexes only solve issues in the moment, not as the workload evolves.
These limitations show up quickly in day-to-day operations. Teams often see:
- Performance that varies from hour to hour across environments.
- Slowdowns involving multiple factors — CPU, I/O, joins, skewed stats, and concurrency.
- OLTP and analytics workloads competing for resources.
- Limited visibility into how live workload pressure affects query behavior.
This is exactly where AI makes a difference. AI SQL optimizers in Oracle 26ai can process huge amounts of telemetry, the kind no human team could ever review in real time. They learn patterns, spot inefficiencies, and adjust execution plans automatically. Instead of reacting after something slows down, the optimizer adapts as conditions change.
Comparison table: Traditional vs AI-driven SQL optimization
To really understand what Oracle 26ai changes, it’s useful to compare it with how SQL tuning has worked for decades. Here’s a quick side-by-side look at how manual tuning stacks up against AI-driven optimization.
| Aspect | Traditional SQL tuning | AI-Driven (Oracle 26ai + dbForge AI Assistant) |
|---|---|---|
| Query tuning | Manual rewrites, hints, and trial-and-error | AI optimizer adjusts plans automatically based on workload patterns |
| Indexing strategy | DBA-created indexes; periodic cleanup | Automatic Indexing evaluates, creates, and retires indexes continuously |
| Execution plan stability | Prone to regressions as data grows | AI predicts changes and stabilizes plans proactively |
| Performance diagnostics | Requires AWR/ASH review and deep manual analysis | Real-time anomaly detection with root-cause suggestions |
| SQL generation | Hand-written queries; high cognitive load | Natural-language SQL generation with optimized structures |
| Adaptability to workload changes | Slow—requires manual tuning after shifts | Self-learning engine adapts automatically as workload evolves |
| Developer/DBA effort | High involvement is needed for each optimization cycle | Minimal—AI handles tuning while teams validate and refine |
| Optimization speed | Hours to days, depending on complexity | Near-instant AI recommendations and automated fixes |
| Accuracy of improvements | Depends on experience and manual analysis | Predictive, data-driven, pattern-aware optimization |
| Scalability across databases | Limited; each platform tuned separately | With its AI-powered capabilities, dbForge Edge brings AI-assisted SQL to Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server. |
| Insight into query behavior | Requires manual plan interpretation | Visual plans + AI explanations highlight bottlenecks instantly |
| Consistency and repeatability | Varies by team skill and workload pressure | AI ensures consistent, repeatable optimization across environments |
Core AI features enhancing SQL optimization
The following features illustrate how 26ai brings AI directly into SQL execution. Many of these capabilities are available across Oracle Database deployments, with the most advanced automation surfaced in Oracle Autonomous Database and 26ai-based cloud services.
AI vector search and semantic indexing
With vector search built into Oracle 26ai, SQL can finally understand context, not just exact values. Oracle makes this possible by storing embeddings internally, allowing queries like “show customers similar to this one” to return semantically relevant matches.
Think of it this way: while traditional indexes work like a dictionary lookup, vector indexes work like a recommendation engine. This opens the door to smarter personalization, better anomaly detection, and richer analytics.
Autonomous SQL tuning and execution plan optimization
Oracle’s autonomous SQL tuning uses machine learning to continuously analyze workloads and optimize queries without human intervention. It includes several self-managing capabilities:
- Automatic Index Creation (AIC): Oracle’s built-in indexing engine that identifies frequently scanned columns and automatically creates the indexes they need.
- Adaptive Query Plans: A runtime optimization feature that adjusts execution strategies on the fly based on real workload statistics.
- SQL Plan Management (SPM): A stability-focused framework that preserves trusted execution plans to prevent regressions as data grows or changes.
Rather than waiting for slow queries to surface, the system reviews workload patterns and continuously refines how queries are optimized.
Generative AI for SQL code suggestions
With an integrated AI assistant, generative AI becomes part of the development workflow. Developers can simply describe their intent in natural language. For example, “find the top 10 customers by revenue growth last quarter,” and receive optimized SQL instantly.
Benefits include:
- Fewer syntax and join errors.
- Cleaner, more efficient query structures.
- Faster iteration for complex analytical tasks.
For example, the prompt above might produce an output like the following code.
SELECT customer_id, revenue_growth
FROM sales_growth
WHERE period = 'Q4'
ORDER BY revenue_growth DESC
FETCH FIRST 10 ROWS ONLY; With an integrated AI assistant, generative AI becomes part of the development workflow. Developers can ask natural-language questions—like “Which actor has acted in the most films?”—and receive accurate, optimized SQL immediately.
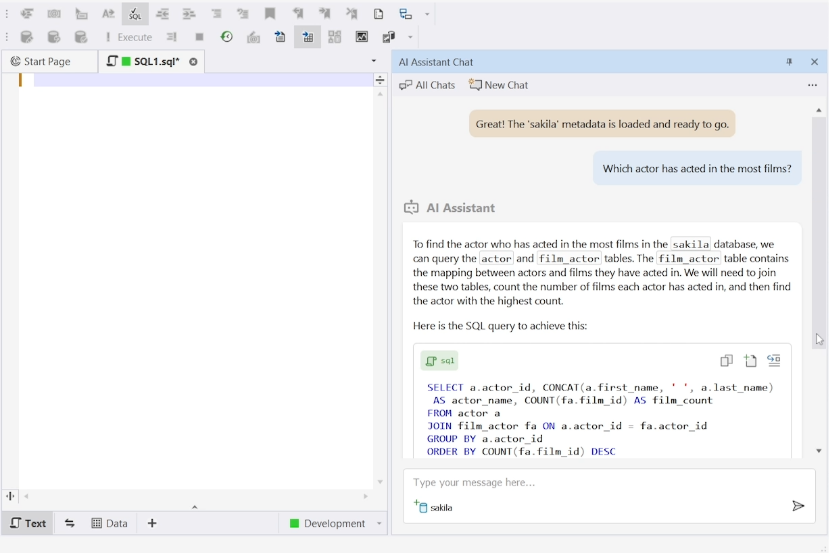
Predictive resource management and workload optimization
Oracle’s AI monitors workload patterns continuously and predicts when demand will spike. It can pre-allocate CPU, memory, and I/O resources before bottlenecks occur, keeping OLTP workloads responsive and ensuring analytical workloads maintain steady throughput during heavy concurrency.
Intelligent query diagnostics and self-healing mechanisms
Oracle 26ai doesn’t stop at detecting problems; in many cases, it can propose or apply fixes automatically. By scanning performance metrics in real time, the database identifies recurring issues such as inefficient joins, missing indexes, or skewed statistics and applies corrective actions automatically. Over time, the system builds a library of patterns it can “self-heal” without manual intervention.
Unified AI integration for structured and unstructured data
The platform’s unified AI engine brings relational tables, JSON documents, vector embeddings, and text analytics into a single environment. With AI models running inside the database, there’s no need for external ML pipelines or duplicated data stores. Developers can query structured and semantic data together, simplifying architecture and enabling AI-driven applications to operate at full speed.
Practical use cases: Oracle AI in SQL optimization
The following examples show how an integrated AI assistant, applies AI-driven intelligence in real workloads. These use cases highlight how everyday performance issues (slow queries, unstable plans, unexpected spikes) are handled proactively rather than through manual tuning.
It’s worth noting that 26ai now unifies relational data, JSON, vectors, graph, spatial data, and text in a single engine. This means the following AI capabilities don’t operate in isolation; they work across every data type without requiring movement to external systems or ML pipelines. Let’s explore!
Automated query tuning and self-learning optimization
In environments where workloads shift constantly, queries may slow down due to changes in data distribution or concurrency patterns. Oracle 26ai picks up on these shifts automatically.
The system learns from signals such as:
- CPU utilization.
- I/O waits.
- join selectivity.
- runtime statistics.
Using these patterns, AI can adjust execution plans, rewrite inefficient statements, or create missing indexes, often before users notice a slowdown.
Because 26ai builds on Oracle’s unified data engine, these optimizations apply consistently across relational queries, JSON operations, vector queries, and mixed workloads, giving teams a more predictable performance profile.
Real-time query diagnostics and anomaly detection
Performance issues rarely show up gradually. A single deployment, data load, or problematic join can spike latency instantly. Oracle 26ai monitors workloads in real time and flags anomalies such as:
- Sudden response-time jumps.
- Excessive buffer gets.
- Lock chains or blocking sessions.
- Skewed or stale statistics.
When something looks abnormal, the AI identifies the likely cause and surfaces the recommended fix inside the AI Assistant. What used to require digging through AWR/ASH reports becomes immediate, actionable insight.
Generative SQL assistance for developers and analysts
Many developers know the answer they want — it’s the SQL that takes time. With the Oracle AI Assistant, they simply describe intent:
“Find the top 10 customers by revenue growth last quarter.”
The assistant generates optimized SQL, applies best-practice join logic, and avoids syntax issues. Analysts and less SQL-experienced team members can produce high-quality queries without waiting for senior or DBA support. This fits into Oracle 26ai’s broader vision: LLM support and in-database AI copilots make natural-language querying a core part of the platform, not just an add-on.
With dbForge AI Assistant, Oracle teams benefit from a faster, more efficient workflow powered by intelligent, task-level automation.
Intelligent indexing and data partitioning
Indexes that boosted performance three months ago may slow you down today. Oracle’s Automatic Indexing continuously evaluates index usefulness, identifies structures that no longer help, and replaces or drops them.
If large tables begin to strain analytical queries, AI recommends partitioning strategies to reduce I/O and improve scan efficiency.
Because indexing and partitioning decisions now operate across all data models (relational, JSON, vector, even spatial), developers no longer need separate tuning approaches for each workload type.
Predictive query caching and resource allocation
Workloads tend to follow rhythms: morning login surges, afternoon analytics, and end-of-month reporting. Oracle 26ai learns these patterns.
It predicts:
- Which queries are likely to run again?
- When will resource-intensive workloads hit?
- Which sessions will need CPU or memory priority?
AI can pre-cache results for recurring analytical queries, pre-allocate CPU or memory before expected load, and maintain consistent performance during peak hours.
This predictive layer supports transactional, analytical, and vector workloads, providing teams with greater stability during demand spikes.
Best practices for using AI in SQL optimization
AI can transform how SQL is tuned and managed in Oracle environments, but it delivers the best results when teams apply it with structure and intention. The following best practices help ensure AI-powered optimization stays safe, accurate, and aligned with real workload needs.
1. Keep human oversight in the loop
AI can generate tuning recommendations, rewrite SQL, and adjust execution plans, but DBAs should always stay involved. Here’s what teams must do:
- Review AI-generated recommendations before applying them to production.
- Confirm that new indexes or rewritten SQL align with business rules & application logic.
- Use AI’s suggestions to accelerate decision-making, not replace human judgment.
AI identifies patterns; humans understand context. Blending both avoids unintended performance or data integrity issues.
2. Manage security, privacy, and model transparency
Oracle’s AI runs inside the database engine, reducing data movement and exposure. This design is reinforced by a secure AI framework that keeps model execution within the database environment, further simplifying compliance. However, AI-assisted tuning must still align with your security and governance standards. Keep the following in mind:
- Keep AI-driven processing and data access confined to Oracle’s secured environment.
- Apply role-based permissions to control who can view or apply AI-generated changes.
- Maintain audit trails so teams can trace what adjustments were made and why.
- Validate that AI-assisted actions comply with internal governance and regulatory requirements.
Strong oversight ensures performance improvements don’t come at the cost of security or compliance.
3. Measure ROI and performance gains
AI delivers the most value when its impact is measurable. To capture those gains, focus on the following:
- Compare query runtimes before and after AI-driven tuning.
- Track reductions in CPU, memory, and I/O consumption.
- Monitor plan stability to ensure improvements hold under peak workloads.
- Measure developer productivity gains when AI generates SQL or tuning insights.
- Use dashboards and reports to visualize improvements over time.
Clear metrics help validate success, justify continued AI adoption, and refine optimization strategies.
Download the AI-powered dbForge Studio for Oracle, launch dbForge AI Assistant, and start generating and optimizing SQL in minutes.
How dbForge tools empower AI-driven SQL optimization
Oracle delivers powerful in-database intelligence, and dbForge solutions help teams take full advantage of it. Together, dbForge AI Assistant, and dbForge Studio for Oracle, or dbForge Edge simplify SQL development, improve performance visibility, and extend AI-assisted workflows across multiple databases. Let’s take a closer look at what each does.
dbForge AI Assistant (Natural-language SQL generation):
- Writes SQL faster with fewer mistakes by turning plain-English prompts into accurate, schema-aware queries. As a result, this cuts SQL creation time by 30–50%.
- Improves code quality with AI-driven suggestions that surface missing joins, risky clauses, and performance anti-patterns, helping teams reduce SQL errors by 20–40%.
- Accelerates debugging and refactoring by explaining complex logic, highlighting problematic areas, and recommending fixes. This reduces troubleshooting time by 40–60%.
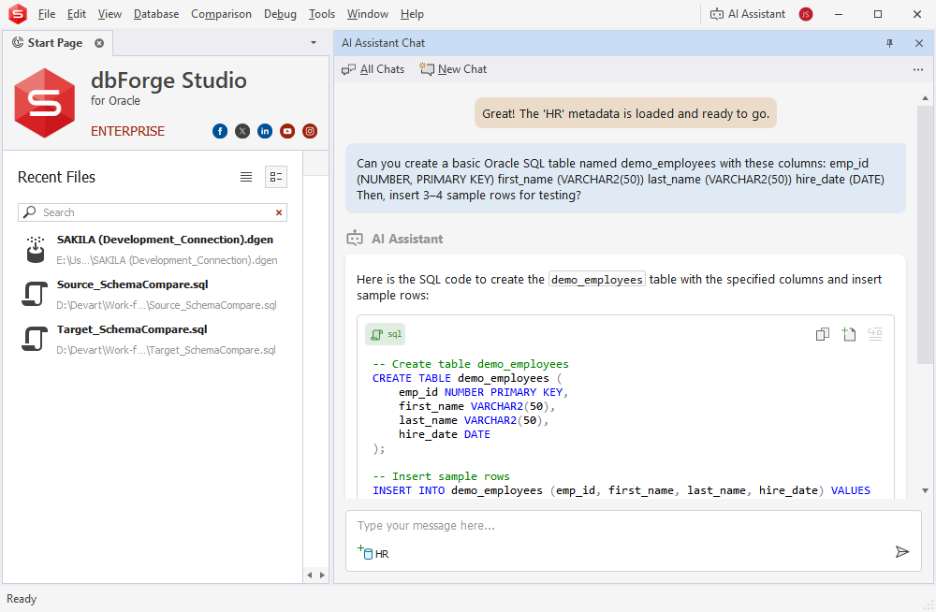
dbForge Studio for Oracle (Visual tuning and diagnostics):
- Shows execution plans in a clear, visual format.
- Highlights slow operations and missing optimization opportunities.
- Benchmarks query performance before and after changes.
As an Oracle SQL IDE, dbForge Studio for Oracle gives developers deep visibility into how their queries behave and why.
dbForge Edge (Multi-database AI-assisted development):
- Supports Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server in one solution.
- Offers AI-assisted SQL across engines for consistent workflows.
- Ideal for multi-DB teams projects.
This universal database tool helps organizations standardize development and maintain consistency across mixed database environments.
Final word
AI-powered SQL optimization marks a clear shift in how performance work gets done. Instead of reacting to slow queries or guessing which indexes might help, teams can lean on Oracle’s AI-native capabilities to learn from workloads, spot issues early, and improve execution paths automatically. It’s a new model of database performance: one that is proactive, adaptive, and built directly into the engine.
For teams looking to get even more from these capabilities, dbForge AI Assistant brings AI-powered SQL generation, optimization, and troubleshooting directly into their Oracle workflows.
This is the right moment to start building with AI-driven workflows, not later.
Download the AI-powered dbForge Edge (free trial available) and begin exploring how AI can elevate both your Oracle SQL and your database operations.
FAQ
Can Oracle AI optimize SQL queries in real time?
Yes. Oracle AI includes an AI SQL query optimizer that continuously analyzes workload patterns, adjusts execution plans, and applies tuning decisions automatically. This real-time optimization reduces latency and stabilizes performance without manual tuning.
What are the main features of Oracle AI Database for SQL developers?
The Oracle AI Database offers autonomous SQL tuning, vector search, predictive resource management, and AI for Oracle SQL generation through natural-language prompts. Developers benefit from faster optimization, fewer regressions, and more accurate execution plans.
What role do AI agents play in Oracle’s new data platform architecture?
AI agents support key Oracle AI use cases such as real-time diagnostics, anomaly detection, semantic search, and automated SQL rewriting. They act as intelligent co-workers, reducing the need for manual debugging and improving SQL performance at scale.
How does Oracle combine generative AI and machine learning for SQL optimization?
Generative AI powers natural-language SQL creation through solutions like dbForge AI Assistant, while machine learning manages adaptive plans and autonomous indexing. Together, they provide a seamless Oracle SQL AI workflow that minimizes most manual tuning.
How does dbForge help Oracle developers generate optimized SQL queries using AI?
dbForge AI Assistant works as a SQL AI generator for Oracle, turning natural-language prompts into optimized SQL, explaining code, and suggesting performance improvements. It complements AI in Oracle Database by giving developers a smarter, faster query development experience.
What benefits do Oracle DBAs get from using dbForge Edge alongside Oracle AI?
dbForge Edge gives Oracle DBAs a unified environment for working across Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server, while still respecting the unique behavior, syntax, and performance characteristics of each engine. It helps teams compare Oracle workloads with how similar logic runs in other systems, understand optimizer differences, and keep tuning practices consistent across platforms. For Oracle teams adopting AI-driven SQL techniques, Edge becomes the place where AI-generated queries, cross-engine diagnostics, and database-specific optimization insights come together in a single workflow.
Can dbForge AI Assistant work as a SQL generator tool for Oracle developers?
Yes. dbForge AI Assistant functions as an Oracle SQL AI tool that generates, refactors, explains, and optimizes SQL using natural-language instructions. It’s designed for developers working in Oracle environments.
Where can I download a free trial of dbForge AI Assistant or dbForge Studio for Oracle?
To get started, first download the AI-powered dbForge Studio for Oracle from the official Devart website.
Download dbForge Studio for Oracle (Free Trial)
Once installed, you can enable and launch dbForge AI Assistant directly from the main toolbar. For detailed setup guidance, follow the official step-by-step instructions here.

