Most teams never question the JDBC or ODBC drivers they use. If it connects, it’s “good enough.” That assumption can cost more than $14,000 per minute during an outage, according to EMA’s 2024 IT downtime benchmark.
Drivers are more than connectors. They dictate how efficiently data moves between databases, applications, and analytics tools. When overlooked, the entire stack slows down. Breakdowns at this level lead to failed reports, missed deadlines, and avoidable downtime.
This article puts the most common options under the microscope: free vendor ODBC drivers and JDBC drivers. It also measures them against Devart ODBC Drivers, using PostgreSQL benchmarks to show where professional drivers deliver clear advantages
Table of contents- Why Database Drivers Matter More Than You Think
- What Are ODBC and JDBC? A Quick Refresher
- Why Choose Devart ODBC Drivers?
- Devart vs Free Vendor Drivers vs JDBC: Head-to-Head Comparison
- Performance
- Integration & Compatibility
- Security & Compliance
- Support & Maintenance
- Devart ODBC in Action: A Real-World Example
- Performance Benchmark: Bulk Updates
- Conclusion
- FAQ

Why database drivers matter more than you think
Database drivers sit quietly in the background, but they act as the gatekeepers to your data. Every query, every report, and every transaction flows through them before reaching the database. If that gatekeeper is slow, limited, or misaligned with your environment, the consequences ripple across the entire stack.
A poor driver choice often causes:
- Severe performance drag – queries take minutes instead of seconds.
- Distorted analytics – precision is lost in numbers, dates, or text.
- Operational breakdowns – drivers fail under concurrency or bulk imports.
These issues cause dashboards to freeze during board meetings, regulators to question filings due to data mismatches, and ETL jobs to stall halfway through billion-row updates.
At the enterprise level, the stakes grow even higher. Delayed BI reports disrupt trading and logistics, blocked integrations cut off vital insights, and instability drains IT resources that should be driving innovation.
That’s why understanding the difference between ODBC and JDBC drivers and choosing the best one matters. With the proper driver, organizations can safeguard mission-critical workloads, maintain reliable integrations, and establish a foundation for secure, scalable growth across both on-premises and cloud environments.
What are ODBC and JDBC? A quick refresher
ODBC and JDBC are standard database connectivity APIs, but each serves a different purpose depending on the platform and ecosystem.
ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) explained
ODBC stands for Open Database Connectivity, a universal standard developed by Microsoft in the early 1990s. It was designed to enable applications written in various languages, such as C, C++, Python, .NET, and many more, to connect to relational databases using a consistent API. When comparing JDBC and ODBC, ODBC emphasizes cross-language universality, while JDBC is tied to Java.
Because of this broad compatibility, ODBC is still widely used in:
- Business Intelligence tools such as Excel, Power BI, and Tableau.
- Enterprise environments that integrate multiple operating systems and databases.
- Legacy systems where stability and standards compliance are critical.
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) explained
A JDBC is a Java-specific connectivity standard created by Sun Microsystems in the same era. It provides a native, well-structured API for Java applications to interact with relational databases. Within its ecosystem, JDBC offers tight integration, strong performance, and broad adoption across various frameworks, including Spring, J2EE, and Android development.
Its limitation is scope: JDBC is confined to the Java world. While it works efficiently for Java applications, using it outside that context often requires wrappers or additional drivers, making it less practical for heterogeneous enterprise stacks.
Key differences between ODBC and JDBC
ODBC vs JDBC differences remain one of the most debated topics in database connectivity as each standard serves very different environments. To make the contrast clear, the table below provides a structured JDBC vs ODBC comparison across key areas.
| Feature | ODBC | JDBC |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Microsoft, early 1990s | Sun Microsystems, early 1990s |
| Language support | Cross-language: C, C++, Python, .NET, and more | Java-only |
| Platform reach | Works across Windows, Linux, macOS, Unix | Runs where Java runs |
| Primary use cases | BI tools, analytics, integrations, legacy systems | Java apps, Spring, J2EE, Android |
| Flexibility | Broad ecosystem support across stacks | Confined to the Java ecosystem |
| Adoption today | Enterprise standard across industries | Strong in Java-driven projects |
Now that the difference between JDBC and ODBC is clear, let’s examine why Devart ODBC Drivers have become the preferred choice for enterprise environments.
Why choose Devart ODBC drivers?
Devart ODBC drivers are designed for enterprise environments where performance, security, and reliability can’t be compromised. Here’s what sets them apart.
Direct connection mode
The Devart ODBC driver connects directly to the database, eliminating the need for vendor-specific client libraries. That means:
- Simpler setup with fewer moving parts.
- Reduced latency in Docker and cloud deployments.
- Greater reliability by removing extra layers that can break under load.
Full ODBC API compliance
The driver is fully compliant with the ODBC API, ensuring smooth integration across both modern and legacy tools. It works with:
- BI platforms such as Excel, Power BI, and Crystal Reports.
- Development frameworks, including Visual Basic 6 (VB6) and Delphi.
- Mixed enterprise stacks where compatibility is critical.
Enterprise-grade security built in
Security is a core feature, integrated directly into the driver. The Devart ODBC drivers support:
- SSH tunneling and HTTPS proxy connections.
- Enterprise firewall and proxy compatibility.
- Encrypted sessions; ideal for zero-trust architectures.
Advanced configuration & performance tuning
Beyond connectivity, Devart ODBC drivers are engineered for stability under pressure. They provide:
- Batch fetch tuning and multiple connection support for optimized throughput.
- Compatibility modes to support legacy applications without rewriting code.
- Connection pooling that maintains speed and stability even at enterprise scale.
In a JDBC vs ODBC connection comparison, these tuning options give ODBC the advantage, offering flexibility and resilience that JDBC alone cannot match.
While Devart ODBC Drivers deliver advanced features out of the box, the real differences emerge when you compare them directly with free vendor drivers and JDBC.
Devart vs free vendor drivers vs JDBC: head-to-head comparison
At a glance, free vendor drivers or JDBC may seem sufficient, but once workloads scale, performance, compatibility, and compliance gaps surface quickly. The table below compares ODBC vs JDBC vs free vendor drivers across the areas that matter most.
| Feature/criteria | Devart ODBC drivers | Free vendor ODBC drivers | JDBC drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Optimized with internal caching and direct connectivity; stable under heavy load | Adequate for small projects, but performance drops under high concurrency or large datasets | Fast in pure Java environments, but less efficient outside |
| Integration & compatibility | Broad compatibility with BI tools (Power BI, Excel, Crystal Reports), ETL platforms, multiple OS, and programming languages | Works best within the vendor’s own ecosystem; limited cross-platform integration | Java-only; requires wrappers or JNI for use outside the Java stack |
| Security features | Enterprise-grade security: SSH tunneling, HTTPS proxy, SSL encryption, and audit-friendly logging | Basic authentication only; lacks advanced enterprise security | Secure inside Java, but with limited protections outside the Java stack |
| Updates & support | Regular updates, commercial technical support, and certifications with BI/ETL tools | Infrequent updates, community-driven support, and slower bug resolution | Maintained by the Java community; support is limited outside Java environments |
| Advanced features | Direct connection mode (no vendor libraries), bulk operations, Unicode support, full ODBC API compliance | Minimal functionality; no connection retries and limited data type handling | Rich feature set within Java; lacks flexibility for mixed environments |
| Stability under Load | Tested for enterprise-grade concurrency; reliable in mission-critical workloads | Prone to timeouts, memory leaks, and deadlocks under heavy load | Stable in Java applications, but less reliable across cross-platform setups |
| Best use case | Enterprise projects requiring reliability, security, and compliance | Prototyping, small-scale applications, or learning environments | Java-only applications (Spring, J2EE, Android) |
The table makes it clear: while free vendor drivers and JDBC can handle basic or niche scenarios, Devart ODBC Drivers are built for enterprise workloads that demand performance, security, and reliability. The following sections unpack these differences in greater detail.
Performance
In head-to-head ODBC vs JDBC performance tests, ODBC delivers more consistent results across mixed environments, while JDBC peaks only in Java-centric stacks. Devart ODBC Drivers take this further with internal caching and direct connectivity, sustaining stable throughput even under thousands of concurrent queries or bulk operations.
Free vendor drivers, by contrast, perform well in small applications but quickly stall when concurrency increases, causing BI dashboards to lag and ETL pipelines to grind to a halt. JDBC performs well in Java-heavy environments, but its efficiency fades outside that ecosystem, making it less reliable in mixed enterprise stacks.
Integration & compatibility
Devart ODBC Drivers are designed for broad compatibility. They work smoothly across BI platforms, including Power BI, Excel, and Crystal Reports, while also supporting ETL pipelines, multiple operating systems, and various programming languages.
The alternatives are more limited here. Free vendor drivers are often tied to their own ecosystems, offering little flexibility outside them. JDBC provides deep integration with Java frameworks like Spring and J2EE, but requires wrappers or JNI bridges for non-Java workloads, adding complexity instead of reducing it.
Security & compliance
Security has become non-negotiable in data environments, and here, Devart differentiates itself. With SSH tunneling, HTTPS proxy support, SSL encryption, and full logging, its ODBC drivers are designed for enterprises that need to satisfy compliance requirements in regulated industries.
In comparison, JDBC secures connections well within Java stacks, but its protections rarely extend beyond that ecosystem. Free vendor drivers pose an even greater risk: with only basic authentication, they leave data streams vulnerable to interception and make compliance audits difficult, if not impossible.
Support & maintenance
Support is another area where the divide is stark. Devart ODBC Drivers are regularly updated, offer commercial-grade technical support, and are certified for use with various BI and ETL tools, providing enterprises with confidence in their long-term reliability.
Both JDBC and free vendor drivers fall short here: JDBC relies on community maintenance without dedicated enterprise support, while free vendor drivers often see infrequent updates and slow bug resolution.
The takeaway: Free and JDBC drivers provide connectivity, but Devart ODBC Drivers deliver performance, security, and reliability at enterprise scale.

Devart ODBC in action: A real-world example
ODBC tools and drivers should be judged by how they perform in real-world use, not just by their feature lists. Devart ODBC Drivers demonstrate this through consistent, enterprise-grade results from installation to integration and under heavy workloads.
Setting up the Devart ODBC driver
The setup process consists of three stages: installation, DSN configuration, and registering the driver system-wide so that any ODBC-compliant application can use it.
Step 1: Install the Devart ODBC driver
Begin the process with these steps:
- Run the installer: Start with an ODBC driver download from Devart’s website. Get the PostgreSQL package and launch the setup wizard.
- Follow the installation wizard: Proceed through the prompts to begin setup.

- Remove previous versions: If an older driver is installed, uninstall it first. The wizard allows overwriting, but a clean install is recommended.
- Select components: Choose whether to install the 64-bit version and whether to include Help and Manual files.
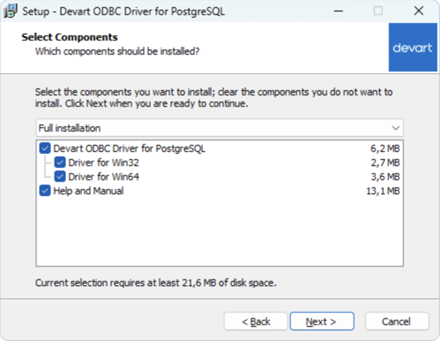
- Activate the driver: Select Trial for evaluation, or choose Activation Key to enter your key from the registration email or Customer Portal.
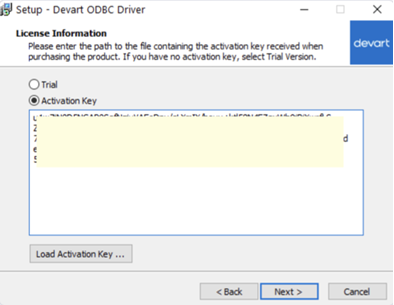
Another way, you can load a saved activation key file.
- Complete the process: Click Next, then Install, and finally Finish to finalize setup.
After installation, proceed to configure the drivers.
Step 2: Configure the DSN
After installation, the next step is to configure a Data Source Name (DSN) so applications can connect through the driver. Here is what to do:
- Open the ODBC Data Source Administrator: Type ODBC Data Sources in the Windows search bar and choose the version matching your application (32-bit or 64-bit). You can also launch it by navigating to Control Panel > Administrative Tools. For direct access, run odbcad32.exe from C:\Windows\SysWOW64 (32-bit) or C:\Windows\System32 (64-bit).
- Select DSN type: Go to the User DSN or System DSN tab. Most applications accept both, though some require a specific type.
- Create a new DSN: Click Add to open the Create New Data Source dialog.
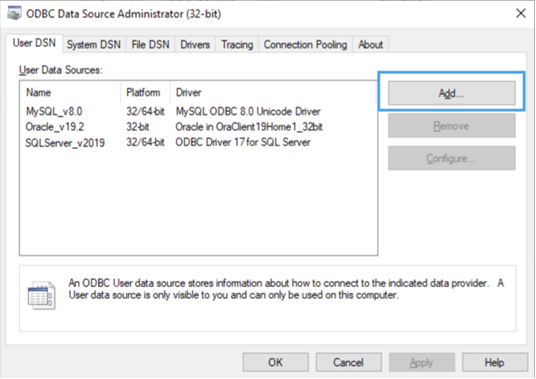
- Choose the Devart driver: Select Devart ODBC Driver for PostgreSQL and click Finish to open the setup dialog.
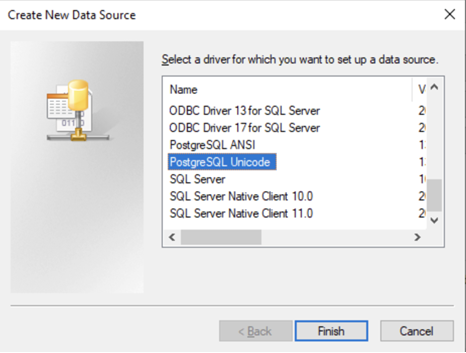
- Enter connection details: Provide the server/host, database name, user ID, password, port, and schema (if required).
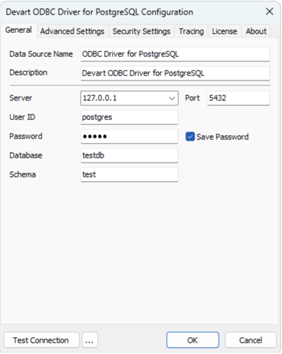
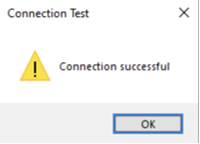
- Test and save: Click Test Connection to confirm, then OK to save the DSN.
Step 3: Integrate with Windows ODBC data sources
Once the DSN is created, the driver becomes visible to any ODBC-compliant tool on Windows.
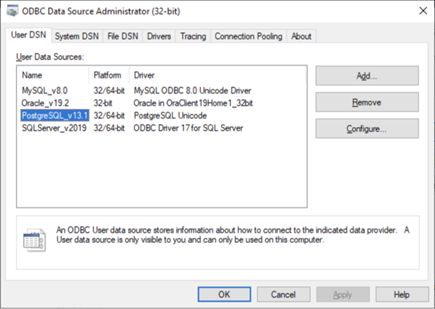
This means:
- BI and analytics tools such as Excel, Power BI, and Tableau can query PostgreSQL directly through the DSN.
- ETL platforms, such as SSIS or Azure Data Factory, can extract data from PostgreSQL and integrate it into pipelines.
- System-wide consistency is ensured, since the DSN is configured once and reused by multiple applications.
Together, these steps transition the driver from installation to enterprise use, establishing a single secure, reusable connection that powers reports, analytics, and data pipelines across your environment.
Connecting to PostgreSQL from Delphi
With the Devart ODBC Driver installed and configured, PostgreSQL can be linked to Delphi applications through the FireDAC framework, which fully supports ODBC connectivity.
Step 1. Prepare the ODBC data source
Ensure the DSN created earlier with the Devart PostgreSQL ODBC driver is available. This DSN will act as the bridge between Delphi’s FireDAC components and PostgreSQL.
Step 2: Create a connection (Delphi / FireDAC)
Add FireDAC components to your project and link them to the ODBC DSN you created. Here is how:
- Open your Delphi project.
- Drop a
TFDConnectioncomponent onto the form or data module. - Drop a
TFDPhysODBCDriverLinkcomponent to enable ODBC connectivity. - In the Object Inspector, set the connection to use ODBC and specify the PostgreSQL DSN.
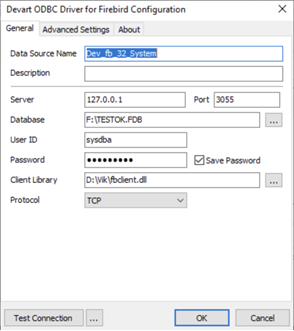
Step 3. Enter the connection details
Configure which DSN to use and supply authentication details. Do the following:
- Double-click the
TFDConnectioncomponent to open the Connection Editor. - From the dropdown, select the Devart PostgreSQL DSN created earlier.
- Enter username and password if they weren’t stored in the DSN.
- Test the connection directly inside Delphi.
- Drop a
TFDQuerycomponent, link it to the connection, and run a SQL query (e.g.,SELECT * FROMcustomers). - Bind the dataset to UI components such as grids or reports to display live PostgreSQL data.
Performance benchmark: bulk updates
One of the most telling benchmarks for any database driver is how it handles large-scale updates. Devart ODBC Drivers are optimized for throughput under load, and PostgreSQL testing demonstrates that advantage clearly.
- Updating 1M+ rows in seconds: In benchmark tests, Devart ODBC Drivers updated over 1 million rows in roughly 12 seconds. This level of performance ensures that nightly ETL jobs, data warehouse refreshes, and transactional workloads complete within narrow batch windows.
- Direct connection mode for lower latency: Unlike many free vendor drivers, Devart ODBC Drivers support direct connection mode, which eliminates the need for client libraries. This reduces latency, simplifies deployment in containerized or cloud environments, and removes common points of failure.
- Minimal resource consumption under load: The driver sustains high throughput without exhausting CPU or memory resources. This makes it suitable for enterprise-grade workloads where stability is as critical as speed, such as real-time analytics pipelines or multi-user reporting environments.
The result: Devart ODBC Drivers deliver both speed and reliability, turning what is often a bottleneck in data workflows into a competitive advantage.
Conclusion
Free vendor and JDBC drivers are effective in limited contexts. But as workloads scale, their trade-offs become clear: performance bottlenecks, integration gaps, and compliance risks. For enterprises, these issues translate into downtime, lost productivity, and hidden costs.
Devart ODBC Drivers are designed to eliminate those risks. With enterprise-grade performance, advanced security, and certified compatibility across BI and ETL platforms, they provide a reliable foundation for data-driven operations.
Watch the webinar below to see the PostgreSQL demo and benchmarks, and evaluate how the right driver choice impacts performance, reliability, and ROI.
For teams evaluating driver strategy in 2025, this choice defines not just today’s performance but the long-term reliability of the entire data stack.

FAQ
What does ODBC stand for?
ODBC stands for Open Database Connectivity, a Microsoft standard from the 1990s that lets applications in different languages connect to relational databases through a common API.
ODAC vs ODBC: what’s the difference?
ODAC is Oracle-specific, while ODBC is vendor-neutral and works across multiple databases and BI tools, making ODBC better for mixed environments.
JDBC vs ODBC performance: which is better?
JDBC performs well in Java-only environments, but ODBC delivers faster, more consistent performance in cross-platform or high-load enterprise systems.
When should businesses switch from free vendor ODBC drivers to commercial solutions?
Free drivers work for prototypes, but in production they often fail under load, lack security, or provide no reliable support. That’s when commercial drivers become essential for stability and compliance.
How do Devart ODBC drivers improve performance in high-load environments?
Devart drivers use direct connection mode, caching, and optimized batch operations to cut latency and handle millions of rows efficiently. The result: faster ETL runs and stable concurrency.
Which industries benefit most from enterprise-grade ODBC drivers with built-in security?
Finance, healthcare, government, and telecoms, any sector needing encryption, tunneling, and compliance-ready logging to protect sensitive data.
Can Devart ODBC drivers integrate with BI tools like Power BI, Excel, or Tableau?
Yes. Devart drivers are certified with major BI platforms, enabling real-time queries from tools like Power BI, Excel, and Tableau through a single DSN connection.

