C++ Builder supports iOS and Android application development since version XE6. This article discusses the basics of developing database applications for iOS and Android in C++ Builder using UniDAC.
UniDAC is a suite of universal data access components for connecting to SQL Server, SQLite, Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, SAP ASE, xBase (DBF), Amazon Redshift, and InterBase from iOS and Android (you can use UniDAC to develop Windows applications that connect to almost any popular database, but this is beyond the scope of this article).
Connecting to a Database
You can access a database from iOS or Android in almost the same way you access it from Windows, but you should be aware of some aspects of connecting and deploying files to a mobile device when working with a local database. This article contains connection instructions and sample code for each database supported by UniDAC.
Connecting in Design-time
Let’s create an Android application that connects to MySQL. Select File > New > Multi-Device Application – C++ Builder.
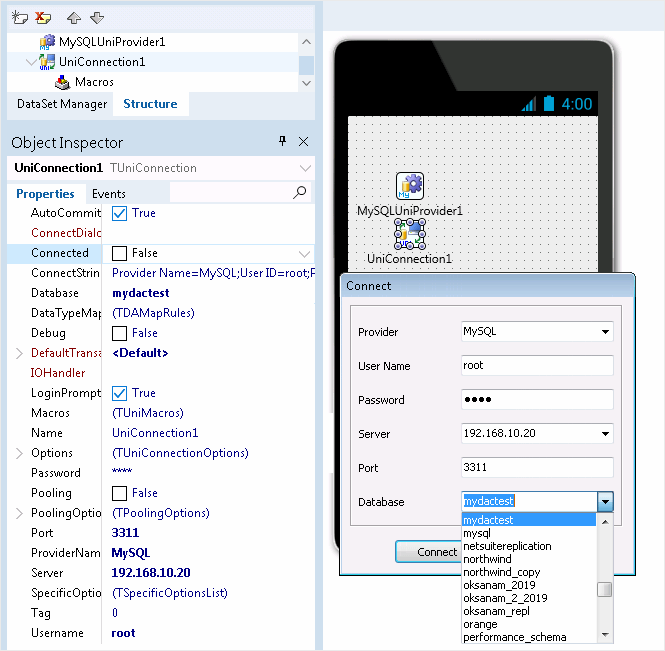
Select Blank Application, then place the TUniConnection and TMySQLUniProvider components onto the form. Set the ProviderName property of TUniConnection to MySQL and assign values to the Username, Password, Server, and Port properties.
You can test database connectivity by setting the Connected property to True. If the values specified are correct, you will be able to view the list of available databases in the Database dropdown.
Compiling the Project
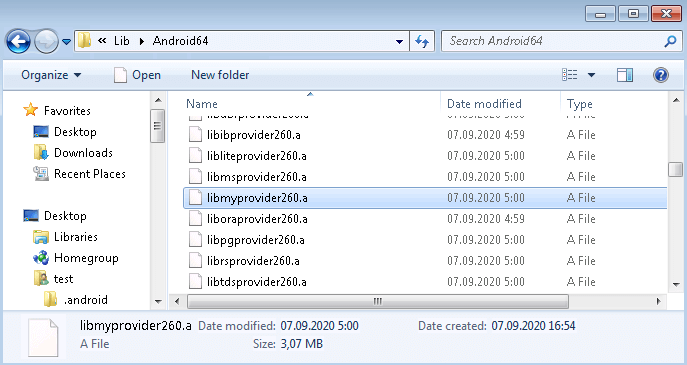
Select Project > Add to Project… and add the MySQL provider library, which is located in “C:\Program Files (x86)\Devart\UniDAC for RAD Studio 10.3\Lib\Android64”. For C++ Builder 10.3 Rio, the filename is libmyprovider260.a.
The table below contains database servers and their corresponding provider libraries for mobile application development in C++ Builder 10.3 Rio using UniDAC.
| Database System | Standard Edition | Professional Edition |
|---|---|---|
| ASE | libaseprovider260.a | libtdsprovider260.a |
| SQL Server | libmsprovider260.a | libtdsprovider260.a |
| SQLite | libliteprovider260.a sqlite3.o |
|
| MySQL | libmyprovider260.a | |
| Oracle | liboraprovider260.a | |
| PostgreSQL | libpgprovider260.a | |
| InterBase ToGo | libibprovider260.a | |
| Amazon Redshift | librsprovider260.a libpgprovider260.a |
|
| xBase | libdbfprovider260.a libvquery260.a sqlite3.o |
If you don’t add this file to the project, you will get an error message during compilation:
“[ldandroid Error] C:\Users\Public\Documents\Embarcadero\Studio\14.0\PlatformSDKs\android-ndk-r9c\toolchains\arm-linux-androideabi-4.6\prebuilt\windows\bin\arm-linux-androideabi-ld.exe: .\Android\Debug\Unit1.o: in function _ZTX6TForm1:.\Android\Debug\Unit1.o.ll(.data.rel.ro._ZTX6TForm1+0x6): error: undefined reference to ‘vtable for Mysqluniprovider::TMySQLUniProvider'”
Compile the project.
Connecting in Run-Time
Put the needed providers onto the form and add their library files (similar to what you did in design-time). Note that despite having the same name, the provider libraries for Android and iOS are different and located in their respective folders:
“C:\Program Files (x86)\Devart\UniDAC for RAD Studio 10.3\Lib\Android64”
“C:\Program Files (x86)\Devart\UniDAC for RAD Studio 10.3\Lib\iOSDevice64”
You need to either place the TUniConnection component onto the form or add the following lines to the header file:
#include "DBAccess.hpp" #include "Uni.hpp"
and the following lines to the cpp file:
#pragma link "DBAccess" #pragma link "Uni"
If you are planning to use a local database on a mobile device, add this line to the header file to get access to the IOUtils namespace:
#include <System.IOUtils.hpp>
ASE
ASE has no client for Android or iOS, therefore a connection to an ASE server can only be established directly via TCP/IP by setting the Direct property to True:
SpecificOptions->Values["Direct"] = "True";
Sample
TUniConnection * Connection;
Connection = new TUniConnection(Form1);
try {
Connection->ProviderName = "ASE";
Connection->Server = "server";
Connection->Username = "user_name";
Connection->Password = "password";
Connection->Database = "database_name";
Connection->SpecificOptions->Values["Direct"] = "True";
Connection->Connect();
ShowMessage("Connected successfully");
}
__finally {
Connection->Free;
}
SQL Server
SQL Server has no MS SQL Native Client for Android or iOS, therefore a connection to SQL Server can only be established directly via TCP/IP by setting the Provider property to prDirect:
SpecificOptions->Values["Provider"] = "prDirect";
Sample
TUniConnection * Connection;
Connection = new TUniConnection(Form1);
try {
Connection->ProviderName = "SQL Server";
Connection->Server = "server";
Connection->Username = "user_name";
Connection->Password = "password";
Connection->Database = "database_name";
Connection->SpecificOptions->Values["Provider"] = "prDirect";
Connection->Connect();
ShowMessage("Connected successfully");
}
__finally {
Connection->Free;
}
SQLite
If you don’t deploy a database with your application, set the ForceCreateDatabase property to True to create a database file automatically when the user first launches your application.
SpecificOptions->Values["ForceCreateDatabase"] = "True"
Sample
TUniConnection * Connection;
Connection = new TUniConnection(Form1);
try {
Connection->ProviderName = "SQLite";
Connection->SpecificOptions->Values["ForceCreateDatabase"] = "True";
Connection->Database = System::Sysutils::IncludeTrailingPathDelimiter(
System::Ioutils::TPath::GetDocumentsPath()) + "db.sqlite3";
Connection->Connect();
ShowMessage("Connected successfully");
}
__finally {
Connection->Free;
}
Oracle
Oracle has no client for Android or iOS, therefore a connection to an Oracle server can only be established directly via TCP/IP by setting the Direct property to True:
SpecificOptions->Values["Direct"] = "True";
To establish a connection to Oracle from Android or iOS, assign your host, port, and service name or system identifier to the Server property.
To connect using the Service Name, the format is as follows:
Server = "Host:Port:sn/ServiceName"; Server = "Host:Port:sn=ServiceName"; (deprecated format)
To connect using the SID, the format is as follows:
Server = "Host:Port:SID"; Server = "Host:Port:sid=SID"; (deprecated format)
If the port number is followed by a colon, and the service name prefix (sn=) or the SID prefix (sid=) is not defined, then by default, the connection will be established using SID. In majority of Oracle servers, the service name is the same as the SID. Consult the Oracle documentation for more information.
Sample
TUniConnection * Connection;
Connection = new TUniConnection(Form1);
try {
Connection->ProviderName = "Oracle";
Connection->SpecificOptions->Values["Direct"] = "True";
Connection->Server = "server:1521:orcl";
Connection->Username = "user_name";
Connection->Password = "password";
Connection->Connect();
ShowMessage("Connected successfully");
}
__finally {
Connection->Free;
}
MySQL
MySQL has no client for Android or iOS, therefore a connection to a MySQL server can only be established directly via TCP/IP by setting the Direct property to True:
SpecificOptions->Values["Direct"] = "True";
Sample
TUniConnection * Connection;
Connection = new TUniConnection(Form1);
try {
Connection->ProviderName = "MySQL";
Connection->SpecificOptions->Values["Direct"] = "True";
Connection->Server = "server";
Connection->Port = 3306;
Connection->Username = "user_name";
Connection->Password = "password";
Connection->Connect();
ShowMessage("Connected successfully");
}
__finally {
Connection->Free;
}
PostgreSQL
UniDAC supports only a direct connection to PostgreSQL, therefore there’s no property that instructs the client on how to connect to the server — you only need to set the server address, port, and the user credentials.
Sample
TUniConnection * Connection;
Connection = new TUniConnection(Form1);
try {
Connection->ProviderName = "PostgreSQL";
Connection->Server = "server";
Connection->Port = 5432;
Connection->Database = "database_name";
Connection->SpecificOptions->Values["Schema"] = "schema_name";
Connection->Username = "user_name";
Connection->Password = "password";
Connection->Connect();
ShowMessage("Connected successfully");
}
__finally {
Connection->Free;
}
InterBase
You can connect to a local or remote InterBase ToGo database from iOS and Android devices.
To connect to a local database, set the path to the database on the device:
Database = System::Sysutils::IncludeTrailingPathDelimiter( System::Ioutils::TPath::GetDocumentsPath()) + "db.gdb";
If you need to establish a connection to a remote server, specify the server address and database name:
UniConnection.Server = "server"; UniConnection.Database = "C:\db.gdb";
Note that the prefix System::Sysutils::IncludeTrailingPathDelimiter (System::Ioutils::TPath:: GetDocumentsPath) is required to connect to a local database.
Local Database Sample
TUniConnection * Connection;
Connection = new TUniConnection(Form1);
try {
Connection->ProviderName = "InterBase";
Connection->Database = System::Sysutils::IncludeTrailingPathDelimiter(
System::Ioutils::TPath::GetDocumentsPath()) + "db.gdb";
Connection->Username = "user_name";
Connection->Password = "password";
Connection->Connect();
ShowMessage("Connected successfully");
}
__finally {
Connection->Free;
}
Remote Database Sample
TUniConnection * Connection;
Connection = new TUniConnection(Form1);
try {
Connection->ProviderName = "InterBase";
Connection->Server = "server";
Connection->Database = "C:\db.gdb";
Connection->Username = "user_name";
Connection->Password = "password";
Connection->Connect();
ShowMessage("Connected successfully");
}
__finally {
Connection->Free;
}
Amazon Redshift
UniDAC supports only a direct connection to Redshift, therefore there’s no property that instructs the client on how to connect to the server — you only need to set the server address, port, and the user credentials.
Sample
TUniConnection * Connection;
Connection = new TUniConnection(Form1);
try {
Connection->ProviderName = "Redshift";
Connection->Server = "server";
Connection->Username = "user_name";
Connection->Password = "password";
Connection->Database = "database_name";
Connection->Port= 5439;
Connection->Connect();
ShowMessage("Connected successfully");
}
__finally {
Connection->Free;
}
xBase
xBase databases don’t use the client-server model, therefore a connection to an xBase database can only be established directly via TCP/IP by setting the Direct property to True:
SpecificOptions->Values["Direct"] = "True";
To connect to an xBase database, you need to set the path to the database and its format.
Sample
TUniConnection * Connection;
Connection = new TUniConnection(Form1);
try {
Connection->ProviderName = "DBF";
Connection->Database = "folder_name";
Connection->SpecificOptions->Values["DBFFormat"] = "dfVisualFoxPro";
Connection->SpecificOptions->Values["Direct"] = "True";
Connection->Connect();
ShowMessage("Connected successfully");
}
__finally {
Connection->Free;
}
Deploying the Application
The deployment of an application to a mobile device is described in the article “How to Develop Android Database Applications in RAD Studio“.
The Difference Between the Android and iOS Application Deployment
The deployment path is different on Android and iOS. If you want to deploy your application to both platforms, make sure that the deployment paths are specified correctly for both Android and iOS.
NOTE: Remember to replace the default value (“.”) of Remote Path with one of the values below.
| С++ Builder Function | Deployment Path | Destination on Device |
|---|---|---|
| TPath::GetDocumentsPath | .\assets\internal | /data/data/com.embarcadero.MyProjects/files |
| TPath::GetSharedDocumentsPath | .\assets | /mnt/sdcard/Android/data/com.embarcadero.MyProjects/files |
Despite having the same name, the providers for Android and iOS are different and located in their respective folders.
Debug
The debugging process is described in the article Remote Debugging of Android Applications in RAD Studio via Wi-Fi
Wrapping up
You can build powerful applications with C++ Builder and UniDAC that work with ASE, SQL Server, SQLite, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, InterBase, Amazon Redshift, and xBase databases from Android and iOS devices.