TL;DR
SQL Server communicates through specific ports, commonly 1433, which can be static or dynamic. This guide explains what these ports do and how to check them using tools like SSMS, Configuration Manager, and dbForge Studio for SQL Server.
The main purpose of SQL Server ports is to receive and transmit data of a certain type. In this article, we will discuss the various types of ports and their differences. We’ll also cover what the default SQL port is, as well as other theoretical aspects.
Moreover, here you will find a practical illustrated guide on how to connect to a port in dbForge Studio for SQL Server.
Table of contents- Introduction
- SQL Server TCP and UDP ports explained
- What is the default port for SQL Server?
- How to configure SQL Server port settings
- How to check what port SQL Server is running on
- Managing SQL Server connections in dbForge Studio
- Conclusion
Introduction
When an application connects to SQL Server, communication happens through a specific SQL Server TCP port. These ports act as numbered gateways that identify how data flows between the client and server. As a rule of thumb, the default SQL port number for SQL Server is 1433, though other static and dynamic ports can be used depending on the configuration.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) officially registers certain port numbers for specific purposes, but in real-world setups, ports may also be used unofficially.
SQL Server TCP and UDP ports explained
SQL Server relies on both TCP and UDP ports for different services. While TCP ports are used for core database connections, the SQL Server UDP ports handle service discovery and auxiliary tasks.
For instance, the default SQL Server port 1433 is reserved for the Database Engine’s default instance and processes incoming TCP requests. On the UDP side, port 1434 runs the SQL Browser service, which helps clients identify the correct instance and its associated TCP port. Beyond these, other ports are assigned to components such as SSRS, SSAS, SSIS, AlwaysOn availability groups, and clustering.
The following table lists the most frequently used SQL Server TCP and UDP ports and their purposes.
| Port Number | Protocol | Purpose |
| 80 | TCP | To publish SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) reports using HTTP |
| 135 | TCP | T-SQL debugging, WMI, MSDTC, Agent file copy |
| 443 | TCP | To publish SSRS reports using HTTPS |
| 500 | UDP | IPSec to encrypt connections |
| 1433 | TCP | Database engine default instance |
| 1434 | TCP&UDP | DAC and the SQL Browse |
| 2382 | UDP | SQL Server Analysis Services with dynamic ports |
| 2383 | TCP | SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) |
| 2725 | TCP | SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) |
| 3343 | UDP | Cluster network driver |
| 3882 | TCP | SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) |
| 4022 | TCP | SQL Broker Service |
| 4500 | UDP | IPSec |
| 5022 | TCP | AlwaysOn |
| 7022 | TCP | Database Mirroring |
| from 1024 to 5000 | TCP | Dynamic ports for named instances |
| from 5000 to 5099 | UDP | Clusters |
| from 8011 to 8031 | UDP | Cluster internode |
| from 49152 to 65535 | TCP | More dynamic ports for named instances |
What is TCP
TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol, designed to manage reliable data transmission on the Internet. It guarantees delivery by retransmitting lost packets and eliminating duplicates. Because it is connection-oriented, data can travel both ways once the connection is established.
What is UDP
UDP stands for User Datagram Protocol, a connectionless protocol that sends data without setting up a session first. This makes it faster but less reliable than TCP.
In SQL Server, UDP is mainly used for service discovery. For example, the SQL Browser service on UDP port 1434 tells client applications which TCP port a given instance is listening on. This is a lightweight exchange that enables quick connections, even when multiple instances run on the same server.
What is the default port for SQL Server?
When SQL Server is installed, the system configures default ports for its services. For the Database Engine, the SQL Server port 1433 is the standard static TCP port. Client applications use this port, along with the server’s IP address, to establish a connection without needing to specify custom settings.
SQL Server supports two types of ports: static and dynamic. The following sections explain how to configure SQL Server static port settings and how SQL Server dynamic ports work.
Static ports in SQL Server
A static port never changes, even after restarting the service or the machine. By default, the MSSQLSERVER instance uses TCP port 1433 as its static assignment. Using a static port makes connections predictable and easier to manage in firewalls.
To configure SQL Server static port:
- Open SQL Server Configuration Manager.
- Select Protocols for MSSQLSERVER in the SQL Server Network Configuration.
- Right-click TCP/IP and choose Properties.
- Assign the desired port under TCP Port in the IP Addresses tab.
- Restart the SQL Server service to apply changes.
Understanding SQL Server dynamic ports
A dynamic port is assigned by the operating system each time SQL Server restarts. Instead of a fixed number, the configuration uses 0 in the port field. When the service starts, the OS allocates an available port from the dynamic range (49152–65535).
SQL Server dynamic ports simplify instance management on systems with multiple SQL Server installations, but they complicate firewall rules since the port may change with each restart. In such cases, enabling the SQL browser port SQL Server (UDP 1434) is essential, since it tells client applications which TCP port the instance is currently using.
SQL Server ports for named instances
Named instances of SQL Server do not use port 1433 by default. Instead, they are assigned dynamic ports by the operating system each time the service starts. This means the listening port can change, which complicates firewall and client configuration.
To make connections more predictable, administrators often reassign a static port to a named instance. In such cases, the SQL Browser service on UDP port 1434 plays an important role: it tells client applications which port the named instance is listening on.
For example:
- A default instance listens on SQL Server port 1433 unless changed.
- A named instance (e.g., SERVERNAME\SQL2019) may be assigned SQL Server dynamic ports unless configured with a static port.
SQL Browser service and port 1434
The SQL Browser service runs on UDP port 1434 and is critical when working with named instances and SQL server dynamic ports. Its job is to listen for incoming client requests and return the TCP port number of the correct SQL Server instance.
Without this service, clients would need to know the exact port number of every instance in advance, which is impractical in environments with multiple instances or dynamic port assignments.
Key points:
- Protocol: UDP only
- Default port: 1434
- Role: Directs clients to the right SQL Server instance and its listening port
- Use case: Essential for connecting to named instances or when ports change dynamically
If the SQL Browser service is disabled or blocked, connection attempts to named instances may fail unless you explicitly specify the port number in the connection string.
Troubleshooting SQL Server port connection issues
When connecting SQL Server to a remote machine, you may encounter the error “1433 SQL Server not listening.” This usually happens when the Database Engine isn’t accepting connections on its default TCP port.
To fix this issue:
- Open SQL Server Configuration Manager.
- In SQL Server Network Configuration, select Protocols for MSSQLSERVER.
- Make sure TCP/IP is enabled.
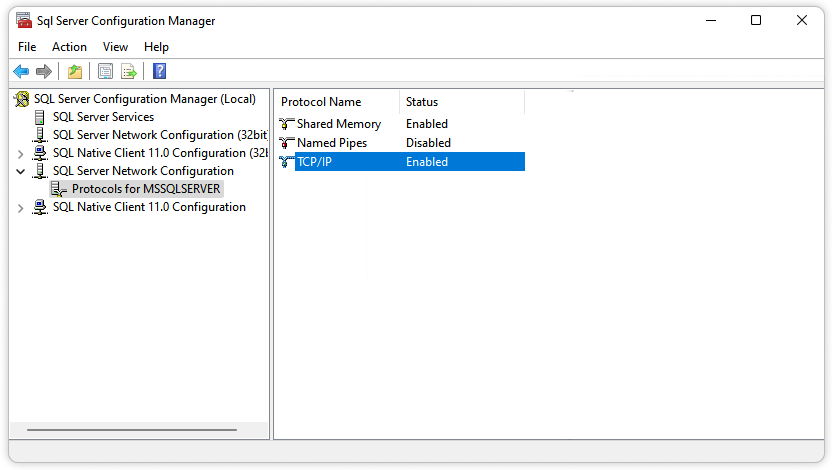
If connections are still blocked, check your firewall settings. You may need to open port for SQL Server in firewall so that external clients can reach the Database Engine. This is especially important when using the default port 1433 or when assigning a custom static port.
How to open a port for SQL Server in firewall
If SQL Server is running but remote clients still cannot connect, the firewall may be blocking the listening port. To fix this, you must allow inbound connections on the port SQL Server is using (commonly SQL Server port 1433, or a custom static port if configured).
Here’s how to configure it on Windows Firewall:
- Open Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Defender Firewall.
- Click Advanced settings.
- In the left pane, select Inbound Rules.
- Click New Rule… in the right pane.
- Choose Port as the rule type and click Next.
- Select TCP and enter the port number (e.g., 1433).
- Choose Allow the connection, then click Next.
- Select the profiles where the rule applies (Domain, Private, Public).
- Give the rule a name, such as SQL Server Port 1433, and click Finish.
Repeat the process for UDP port 1434 if the SQL Browser service is used. Once these rules are in place, remote clients will be able to connect without firewall interference.
How to configure SQL Server port settings
You are not limited to using the default SQL Server port in every environment. Changing the port reduces exposure and is essential when multiple SQL Server instances run on the same host. Here is the SQL server port configuration step by step process administrators should follow:
- Open SQL Server Configuration Manager.
- In SQL Server Network Configuration, select Protocols for MSSQLSERVER.
- Right-click TCP/IP and select Properties.
- Go to the IP Addresses tab.
- Under TCP Port, assign a new port number (you can set one for each IP address or a single port for all).
- Click OK to save.
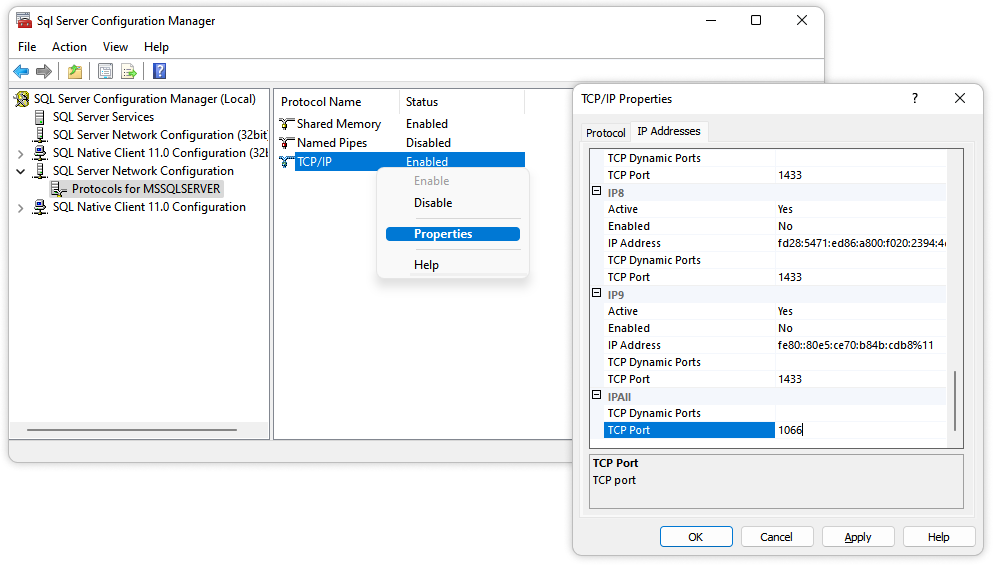
Restart the SQL Server service to apply changes.
Note: When you change the port, remember to update firewall rules to allow incoming traffic on the new number.
How to check what port SQL Server is running on
By default, the SQL Server Database Engine listens on TCP port 1433 and the SQL Browser service uses UDP port 1434. But when you’re managing multiple instances or custom configurations, each instance may listen on a different port. Tracking these can quickly become confusing.
Fortunately, there are several ways to verify the active port for a given instance—using SQL Server tools, Windows utilities, or even the command line. The following methods will help you identify which port SQL Server is currently using:
- SQL Server Configuration Manager
- Event Viewer
- SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
- Command Line
How to check SQL Server port via command line
You can also check the port directly from a command prompt. This is useful when GUI tools aren’t available or when scripting checks across servers. Use the following steps:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Run the following command.
netstat -ano | findstr "1433" Replace 1433 with the port you want to check, or omit it to list all active ports.
- Look for the SQL Server process (sqlservr.exe) in the output to confirm which port it is listening on.
This approach is one of the simplest ways to check SQL Server port CMD, giving you a quick way to validate connectivity issues or confirm custom port settings.
Using SQL Server Configuration Manager to find port number
Earlier in this article, we have already used SQL Server Configuration Manager to configure ports. In a similar way, we can also check the port number without changing it later:
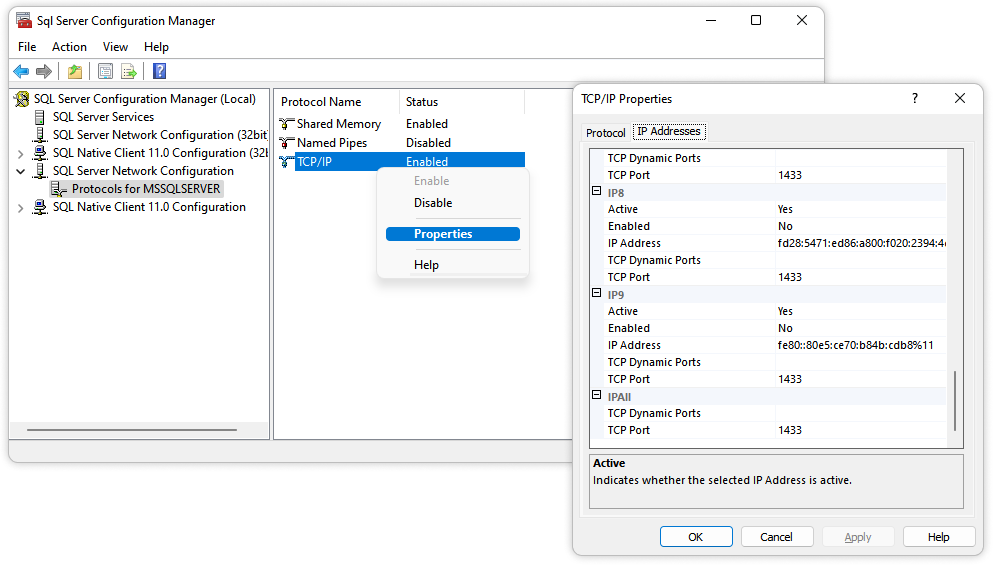
- Open SQL Server Configuration Manager
- In the SQL Server Network Configuration menu, select Protocols for MSSSLSERVER
- Right-click TCP/IP and select Properties
- In the window that opens, click the IP Addresses tab
- Check what port the SQL Server is currently running on
Checking SQL Server port in Event Viewer
Event Viewer is a Windows component that allows administrators to check the logs either on the local computer or on a remote machine.
- Open Event Viewer
- Expand Windows Logs
- Right-click Application
- Click Filter Current Log
- In the window that opens, filter for events with Event ID 26022
- Click OK
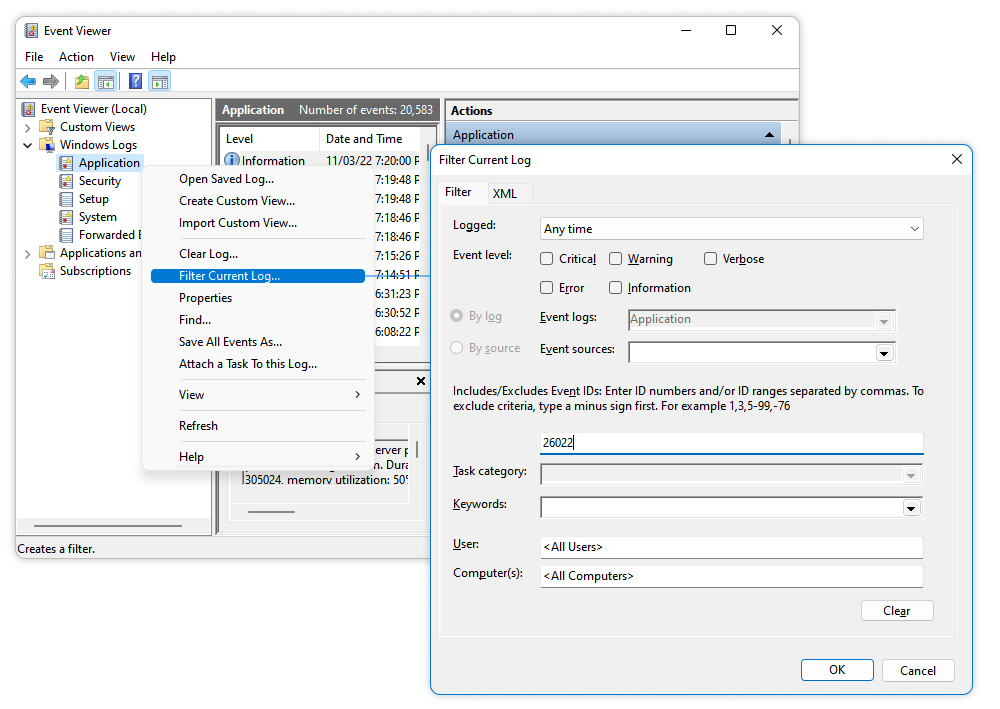
Now, you can only see the events associated with the SQL Server. By clicking each one of them, you will see a message containing the information on what IP and port the Server is listening on.
For example: “Server is listening on [ ‘any’ <ipv4> 1433]“, where:
- ‘any’ <ipv4′ means that the server is listening on any available IP of a fourth version.
- 1433 – is the port number the server is listening on.
![Windows Event Viewer is showing MSSQLSERVER Event ID 26022 with message "Server is listening on [any] <ipv4> 1433".](https://blog.devart.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/current-port-in-event-viewer.png)
Find SQL Server port using SSMS
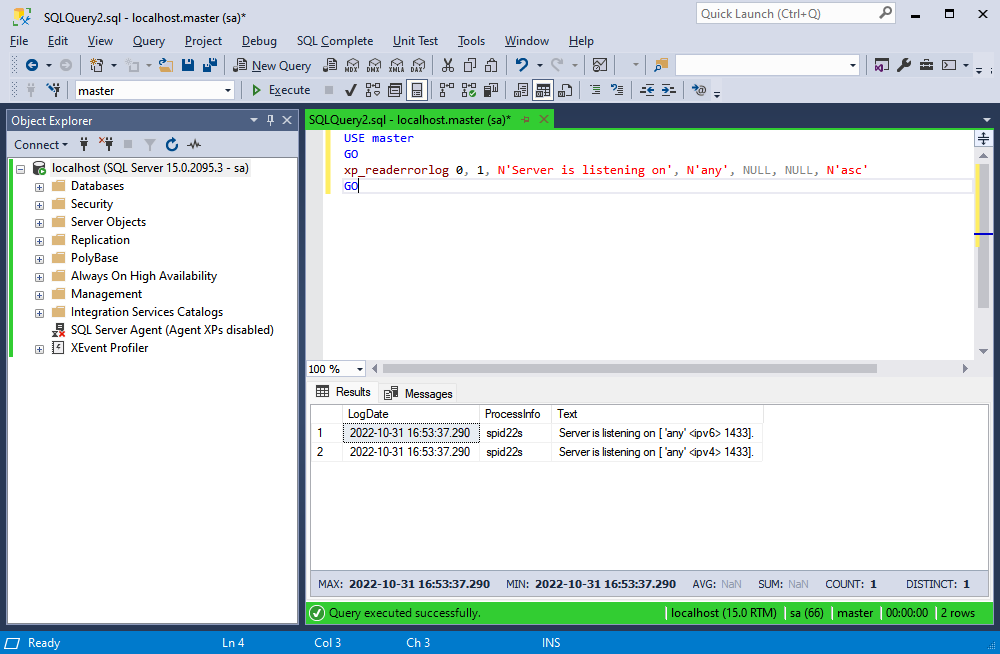
SSMS is one of the most popular tools to work with SQL Server. To check what port the service is listening on, we will be using the following command.
USE master
GO
xp_readerrorlog 0, 1, N'Server is listening on', N'any', NULL, NULL, N'asc'
GO- Copy the command above
- Open SSMS
- Click New Query
- Paste the previously copied command into the SQL document
- Click Execute
On clicking Execute, you will get a message containing the information on what IP and port the Server is listening on.
Managing SQL Server connections in dbForge Studio
With all its merits, SSMS can not always meet all the users’ requirements. There are endless plug-ins out there that can help customize the tool, including dbForge SQL tools, however, it takes time to look for them and go through the installation process. Fortunately, there is a convenient GUI that instantly solves this issue. dbForge Studio for SQL Server has everything you need to set up your SQL development environment.
You can visually manage all the SQL Server connections through Database Explorer. Here, you will see recently used database connections, along with databases and database objects within those.
Create a new database connection
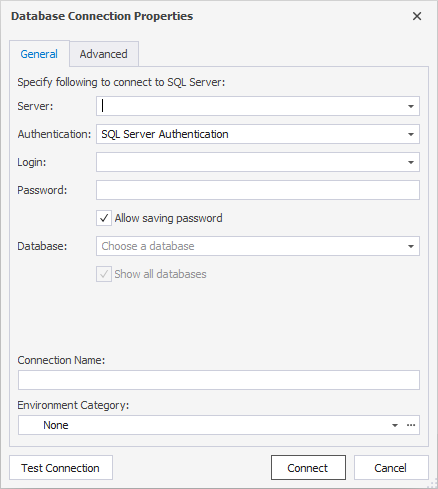
To open the Database Connection Properties window, do either of the following:
- Click New Connection on the Database Explorer toolbar
- Right-click Database Explorer and select New Connection on the shortcut menu
In the Database Connection Properties window that opens, specify the connection details:
- Server: choose the required server from the drop-down list or specify a new one.
- Authentication: choose the authentication mode from the drop-down list.
- Login and Password: type in the user credentials respectively.
- Allow saving password: select if you wish to allow saving the password for further authentication.
- Database: select the database from the drop-down list or enter the name of a SQL database you want to connect to.
- Connection Name: the name of the connection will be generated automatically from the hostname. If you wish to change it, simply type in a new one.
- Environment Category: this step is optional. You can choose the connection category (Development, Production, Sandbox, and Test) from the drop-down list.
Once all the properties have been specified, you can click Test Connection to make sure everything is set correctly. Alternatively, you can simply hit Connect without any double-checking. Rest assured that if there are any issues during the connection, dbForge Studio will provide you with an informative error message.
Modify an existing connection
If you would like to change anything in the connection that already exists, simply right-click it and select Modify Connection.
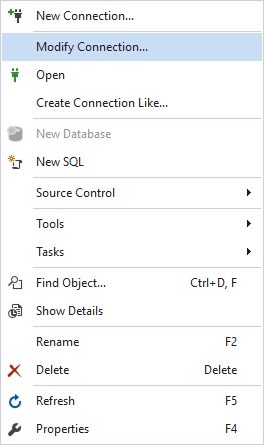
Then, the Database Connection Properties window opens and you can edit any field, just like during the creation of a database connection. Once done, either click Test Connection or Connect.
Open a database connection
There are three ways to open a connection that has been closed:
- Double-click a connection in Database Explorer
- Right-click a connection and select Open
- Select a connection in Database Explorer and click
Close a database connection
To close an open connection, there are two ways:
- Right-click a connection and select Close
- Select a connection in Database Explorer and click
Delete a database connection
In order to delete a connection that you do not need anymore, give it right click and select Delete. To confirm the removal, click Yes in the dialog that opens.
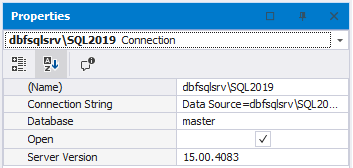
View connection information
In Database Explorer, right-click a connection and select Properties. Alternatively, simply press F4. In the Properties pane that opens, you will see all the information about the connection.
Conclusion
In this article, we have been talking about SQL Server ports, their types, and why they are important for server connection. Moreover, we have looked into a convenient GUI tool that makes working with SQL database connections much easier and user-friendly. Download a fully-functional trial version of dbForge Studio for SQL Server for evaluation purposes.

