It is no longer news that MariaDB 12 has officially landed, and it’s making waves across the database world.
For over a decade, MariaDB has been the go-to open-source database for developers and businesses seeking a stable and innovative MySQL-compatible platform. This new release further enhances its value.
MariaDB 12 delivers major performance upgrades, new features, and significant redesigns to enhance speed, scalability, and developers’ experience. Additionally, it introduces some breaking changes that highlight MariaDB’s continuous commitment to modernization and long-term sustainability.
In this release guide, we’ll walk you through the major innovations and performance breakthroughs that set MariaDB 12 apart. We’ll also explore how these changes can help you design, scale, and optimize your apps more effectively than ever.
Let’s dive in.
- Introduction to MariaDB 12
- MariaDB 12 release overview
- New features in MariaDB 12
- Breaking changes in MariaDB 12
- MariaDB 12 vs MariaDB 11
- MariaDB 12 benchmarks and performance
- How dbForge Studio for MySQL supports MariaDB 12
- Conclusion
- FAQ
Introduction to MariaDB 12
MariaDB is a powerful, open-source, community-driven relational database management system that originated as a fork of MySQL. It was created by the original developers of MySQL to ensure the continued freedom, transparency, and innovation of the database ecosystem. Over the years, MariaDB has evolved into a trusted, enterprise-grade platform, powering applications across industries and cloud environments worldwide.
This new version introduces significant performance improvements, deeper optimizer enhancements, and architectural updates that set the stage for MariaDB’s long-term development roadmap.
The 12.x series marks the beginning of a new generation of releases focused on speed, scalability, and modernization. It paved the way for the next Long-Term Support (LTS) version, MariaDB 12.3.
MariaDB 12.0 became generally available on August 7, 2025. You can read the full announcement and technical MariaDB 12 release notes here.
Now, let’s walk through what this new release entails.
MariaDB 12 release overview
The 12.x series of MariaDB represents the next major evolution of the platform. It is designed on the strengths of the 11.8 line and pushes toward improved performance, stronger scalability, and tighter compatibility with modern database workloads. Here are the things to expect with this new release.
Release family & rolling model
Starting with 12.0, MariaDB shifts into its “rolling release” model. Meaning, incremental updates drop more frequently rather than bundling everything into one large monolithic version. Subsequent 12.x versions, like 12.1 and 12.2, continue to introduce more changes and improvements.
Additionally, each 12.x release (12.0, 12.1, 12.2…) delivers new features, bug fixes, and optimizations, all while maintaining compatibility within the 12.x family. For example, the current 12.x line includes:
- MariaDB 12.0: The initial General Availability (GA) release in the series, introducing the new replication architecture, performance improvements across InnoDB, and updated SQL optimizers.
- MariaDB 12.1: Builds on 12.0 with enhancements such as improved JSON functions, faster query execution for complex joins, and extended system versioning capabilities.
- MariaDB 12.2: Adds higher-level performance tuning features, refined optimizer heuristics, better page compression, and additional security hardening options.
As a developer or DBA, this rolling model gives you faster access to innovation while still staying on a supported major version. Here are the major goals of the MariaDB 12 release model:
- Performance: MariaDB 12 has been engineered with speed and resource efficiency in mind. From optimizer tweaks to more efficient I/O and concurrency handling, the release targets real-world workload improvements.
- Scalability: MariaDB 12 also enhances support for large-scale systems, both in terms of data size and number of concurrent operations. The architecture reflects trends in cloud-native deployments and distributed database usage.
- Compatibility: While pushing forward, MariaDB 12 remains committed to backward compatibility with MySQL data access components and earlier MariaDB releases, but with significant changes and improvements that may require review in migrations or upgrades.
Put simply, MariaDB 12 isn’t just “another version.” It’s the foundation of a modern, continuously evolving release stream, prepared for enterprise-scale demands and the future of data infrastructure.
New features in MariaDB 12
Let’s explore some of the MariaDB 12 new features.
For better understanding, the features are divided into categories to help you digest the major improvements and technical enhancements.
SQL language and engine improvements
- Optimizer improvement: MariaDB 12 optimizer receives extended support for optimizer hints such as QB_NAME(), NO_RANGE_OPTIMIZATION(), NO_ICP(), MRR(), NO_MRR(), BKA(), NO_BKA(), BNL(), NO_BNL(). As a developer or DBA, this improvement allows you more control over query execution.
- Storage engine updates: In MariaDB 12, fixes and enhancements around the Aria and InnoDB engines address buffer pool behaviors, partitioned tables, and foreign key constraints.
- Client/utility enhancements: The mariadb client adds an option –script-dir to specify alternative script directories invoked via source.
- Removal of deprecated system variables: For instance, big_tables, deprecated since MariaDB 10.5, and large_page_size (since 10.5.3) are removed in 12.x.
Example scenario: A query previously suffering from sub-optimal join ordering might now benefit from a hint like NO_RANGE_OPTIMIZATION() to force a better plan. This improvement gives you more control over the SQL engine.
Security and authentication enhancements
In terms of security and authentication, MariaDB 12 comes with the following:
- New support for passphrase-protected keys (MDEV-14091) for stronger encryption of key material.
- The file_key_management plugin (for TDE—transparent data encryption) now supports SHA2 keyed operations.
- A new SQL command,
SET SESSION AUTHORIZATION (MDEV-20299), is introduced to offer more control over session authorization contexts.
For admin and compliance, these enhancements tighten the database’s posture in environments with strict compliance requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Encrypting key material with passphrases, adopting SHA-2 cryptographic schemes, and enforcing fine session authorization mean less manual work and greater alignment with security frameworks.
Performance and scalability upgrades
MariaDB 12 offers the following notable enhancements in terms of scalability and performance:
- The new MariaDB 12 emphasizes real-world workload improvements. For example, the rolling release model allows more frequent performance optimizations.
- MariaDB 12 also comes with large-scale engine tuning, including improved concurrency and buffer management in InnoDB and enhanced partition-to-table conversions. These improvements address edge cases that could crash replicas.
- The upcoming 12.1 preview list highlights features like segmented key cache for Aria and MDL scalability improvements for large-scale systems.
Thanks to these performance upgrades, workloads with high levels of concurrency, large partitions, or heavy replication chains now enjoy measurable throughput and latency improvements. Meaning, less time tuning and more headroom for growth.
Developer & DevOps features
If you are a database developer or DevOps engineer, here are some of the features in the newly released MariaDB 12 that will benefit you greatly:
- Better tooling support: As a developer, with MariaDB 12, you get more options in the client and script execution environments.
- DevOps-friendly release cadence: The 12.x series follows a rolling release model, which means faster delivery of features and fixes. Subsequent 12.x versions, like 12.1 and 12.2, continue to introduce further refinements and improved performance. This approach aligns more naturally with continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) workflows.
- Monitoring & metrics enhancements: While this may not be a headline feature, MariaDB 12 introduces improved instrumentation for the storage engine and replication internals. This improvement gives DBAs deeper visibility into database performance and health.
For DevOps and SRE teams, the introduction of rolling releases and enhanced tooling translates to smoother, more incremental updates, improving automation, CI/CD integration, and overall observability across database environments.
Breaking changes in MariaDB 12
While MariaDB 12 introduces several significant improvements, it also comes with some breaking changes and removals that can affect application behavior, configuration settings, and query compatibility. Therefore, before you upgrade, be sure to review these changes carefully and test your workloads to avoid unexpected failures. Below are the MariaDB 12 breaking changes and removals.
Deprecated and removed features
The features deprecated and removed in MariaDB 12 include:
- System variables removed
The following long-deprecated system variables were dropped in MariaDB 12:
- big_tables (deprecated since 10.5)
- large_page_size (deprecated since 10.5.3)
- slave_parallel_mode (superseded by modern replication options)
As a result, applications relying on these variables in configuration files or initialization scripts will fail to start under MariaDB 12.
- Removed query cache
The legacy query cache, which was already disabled by default since earlier releases, has now been fully removed in MariaDB 12. This implies that any statements or scripts referencing these features will result in an “Unknown system variable” error in MariaDB 12. An example of such a query is
SET GLOBAL query_cache_size = 64M; - Authentication plugin changes
In MariaDB 12, some legacy authentication plugins (e.g., mysql_old_password) are no longer supported. This means that if user accounts were created using these older methods, authentication will fail until credentials are updated to use ed25519, SHA-256, or other modern plugins.
- Optimizer and parser adjustments
Certain optimizer hints and syntax combinations that were accepted in MariaDB 11 are now more strictly validated. For instance, the following hints may raise parsing errors if they are not properly ordered or supported by the engine in use.
SELECT /*+ USE_INDEX(table idx_col) NO_ICP() */ * FROM table; - Removed obsolete replication parameters
Parameters tied to the old replication system (e.g., slave_parallel_threads, slave_domain_parallel_threads) have been replaced by replica_* equivalents. Therefore, any scripts or configuration files using the deprecated variables will fail to load.
Impact on applications
These changes primarily affect:
- Automated deployment scripts that still reference old variable names.
- ORM configurations or stored procedures that depend on removed query cache features.
- Custom monitoring or replication tools that use deprecated replication variables.
Recommended actions
- Review your existing my.cnf or my.ini for deprecated variables.
- Update authentication settings for older user accounts.
- Test your application queries and replication scripts in a staging environment before upgrading production systems.
Note
The MariaDB Upgrade Checker can automatically flag incompatible options and help ensure a smooth migration to version 12.
MariaDB 12 vs MariaDB 11
The table below compares the newly released MariaDB 12 vs. 11.
| Feature | MariaDB 11 | MariaDB 12 | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query performance | Stable, but limited optimization | Improved query execution and a smarter optimizer | Faster response times, better scalability under load |
| SQL syntax | Standard SQL + MariaDB extensions | Extended SQL syntax, new optimizer hints, and stricter parsing | More flexibility and fine-grained control for developers |
| Authentication | Legacy plugins supported | Modern authentication defaults, deprecated legacy methods | Improved security posture and compliance readiness |
| Indexing | Conventional indexing available | Enhanced index handling, better performance with large datasets | Faster joins, reduced I/O overhead |
| Storage engines | Mature but incremental updates | Engine-level improvements for InnoDB and Aria | More stability, better concurrency, and crash recovery |
| Security | Standard TLS & encryption | Stronger TLS defaults, passphrase-protected keys, SHA-2 support | Higher data protection, reduced attack surface |
| Replication | Reliable but less flexible | Refined replication parameters and improved crash recovery | Smoother failover and more predictable performance |
| DevOps & monitoring | Limited built-in integration | New metrics, faster release cadence (rolling model) | Easier automation, continuous delivery alignment |
| Upgrade model | Traditional, major release cycle | Rolling release series (12.x) | Faster access to new features and fixes without full reinstallation |
Why organizations should consider upgrading
If you are yet to start using MariaDB 12, here is something to keep in mind and why you should consider upgrading.
Upgrading to MariaDB 12 is more than a version update; it’s a strategic move toward modern database operations. The new release offers performance gains, tighter security, and a rolling release model that aligns with agile and DevOps-friendly practices. This means that, if your organization scales cloud-native applications or manages data-intensive workloads, MariaDB 12 delivers better control, observability, and future-proofing, ensuring long-term stability without sacrificing innovation.
Upgrading to this version offers more benefits.
MariaDB 12 benchmarks and performance
Performance has always been a core focus of the MariaDB project, and version 12 takes this even further. According to the MariaDB documentation, independent MariaDB 12 benchmarks and community testing indicate noticeable speed gains across analytical, transactional, and mixed workloads, with MariaDB 12 outperforming MySQL by roughly 10–12% in real-world scenarios.
These improvements stem from optimizer refinements, query execution enhancements, and more efficient memory handling within the InnoDB (and Aria) engines. The result is faster query resolution, reduced latency under load, and improved throughput in replication-heavy environments.
Additionally, a user reported that MariaDB 12 completed identical query sets up to 12% faster than MySQL, particularly when executing large joins and aggregate functions. This aligns with MariaDB’s ongoing work on parallel query execution and smarter cost-based optimization.
Implications for you
- Faster response times: With improved throughput and lower latency, applications using MariaDB 12 can deliver snappier user experiences.
- Better scalability: The gains shown in concurrency and large dataset benchmarks suggest 12.x is better suited for growing workloads or high-traffic deployments.
- Headroom for growth: If you’re managing systems today on 11.x, the incremental upgrade to 12.x offers measurable performance rewards, not just new features.
Note
These benchmark summaries are from available documentation and analysis; exact numbers may vary by hardware, workload, engine settings, and dataset size. Therefore, it’s advisable to run a customized benchmark in your environment to see how MariaDB 12 performs.
How dbForge Studio for MySQL supports MariaDB 12
No doubt, MariaDB 12 provides significant improvements, ranging from performance and scalability to syntax and security. But with dbForge Studio for MySQL, you enjoy a better and more improved experience. Whether you’re trying out new MariaDB 12 capabilities or improving production workloads, dbForge Studio provides a comprehensive toolkit that makes every task faster and simpler.
Here are some of the advanced features you’ll get when you connect dbForge Studio for MySQL to MariaDB 12.
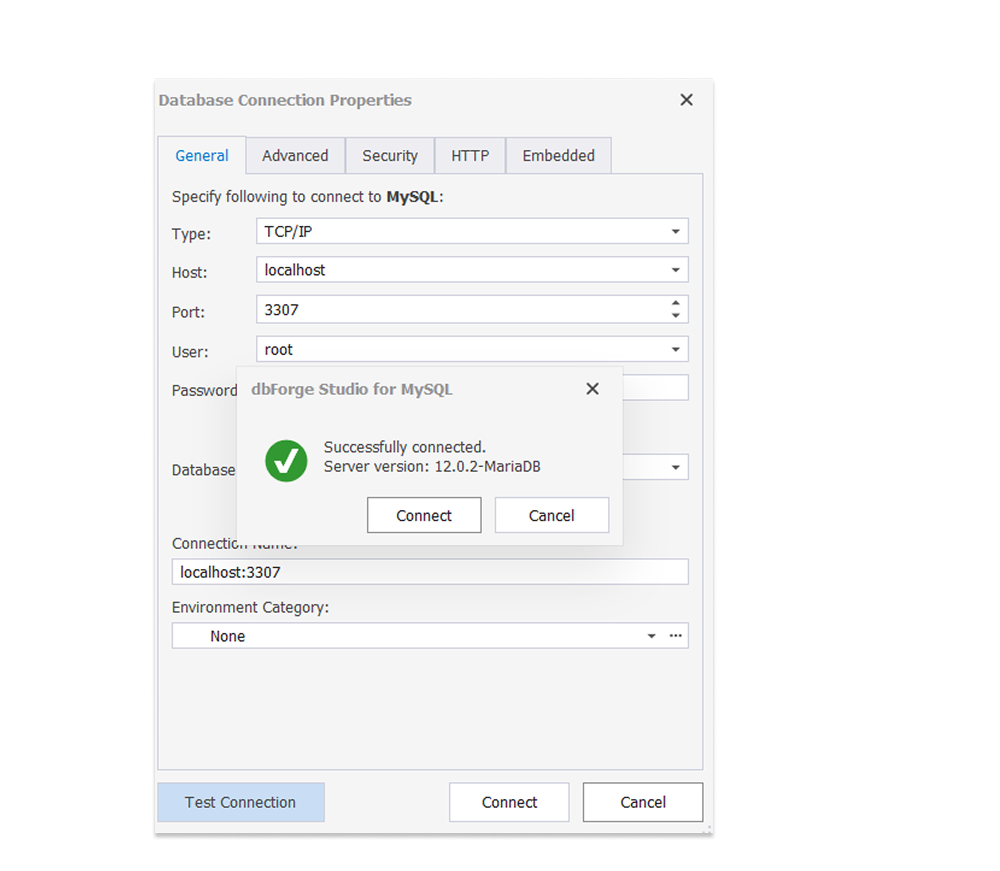
Advanced SQL editor
The dbForge Studio for MySQL is built with a powerful SQL editor that speeds up the writing and optimization of SQL queries with intelligent code completion, syntax highlighting, and real-time error detection. It fully supports MariaDB 12’s new SQL syntax and optimizer hints, allowing you to code confidently while taking advantage of the most recent database improvements.
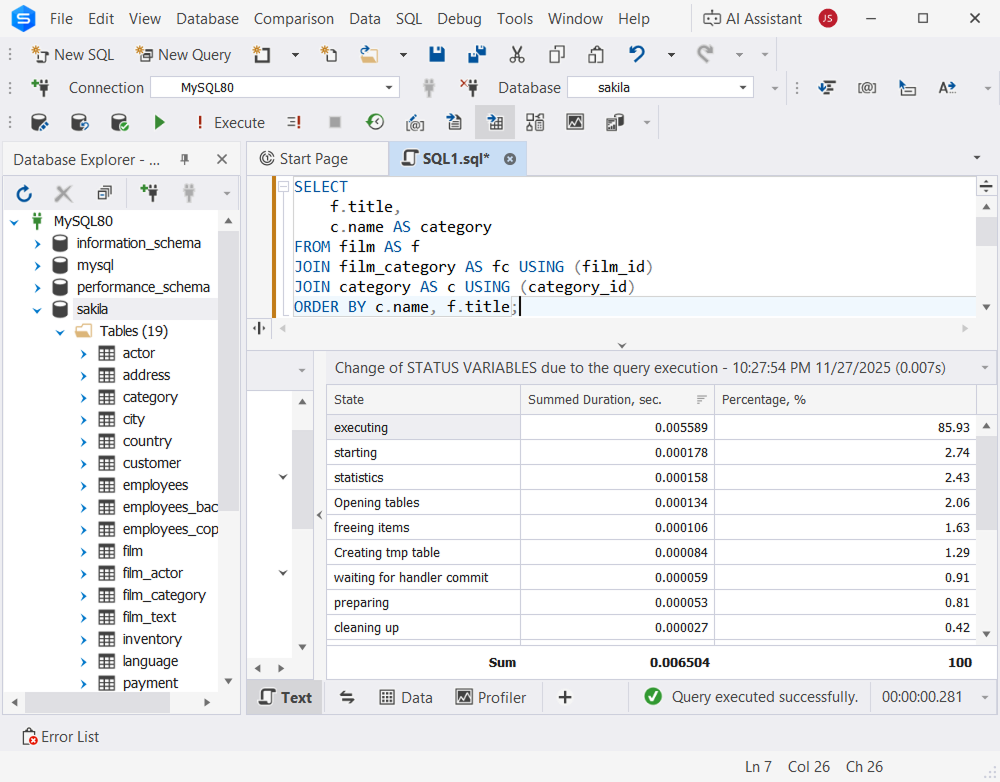
Query Profiler
The dbForge Studio for MySQL also allows you to gain deep insights into your query performance using visual execution plans and detailed profiling metrics. This feature helps you to quickly identify bottlenecks, compare results across different versions, and fine-tune performance for faster and more efficient query execution.
Schema comparison
With dbForge Studio for MySQL, you can easily compare and synchronize database structures and data between MariaDB 12 and previous versions. This feature is invaluable when testing upgrades, validating migrations, or maintaining consistency across development and production environments.

Backup and restore tools
The dbForge Studio for MySQL also lets you protect your MariaDB 12 databases with intuitive backup wizards that simplify both full and incremental backups. You can restore your data in just a few clicks with no manual scripting or complexity.
AI assistant
Here is the best part. With dbForge Studio for MySQL, you can harness the power of the integrated AI Assistant to instantly generate SQL queries, documentation, and code explanations in natural language. This feature is your perfect productivity partner for exploring new MariaDB 12 functionality or troubleshooting complex SQL logic with ease.
Ready to see how it works? Download the free trial of dbForge Studio for MySQL to start working with MariaDB 12 today.
Conclusion
MariaDB 12 is a daring new chapter in the evolution of leading open-source database platforms. It raises the bar for speed, scalability, and developer productivity with improved SQL capabilities, performance advancements, security enhancements, and a modern rollout methodology.
However, despite these impressive new capabilities, MariaDB 12 introduces significant breaking changes and deprecated settings. To ensure a smooth transition from your current version to this new one, make sure to test your applications, review configurations, and check compatibility in a controlled environment.
For developers, DBAs, and organizations eager to upgrade to MariaDB 12, having the right MySQL GUI companion tool is your best bet. dbForge Studio for MySQL provides everything you need to operate confidently with the latest version of MariaDB 12. From intelligent SQL editing and performance profiling to data comparison, backup automation, and AI-powered assistance, dbForge Studio streamlines your database administration process.
Try the AI-powered dbForge Studio for MySQL for free and see how it elevates your experience with MariaDB 12.
FAQ
1. How do I install MariaDB 12 on Linux?
You can install MariaDB 12 from the official MariaDB repositories. First, add the repository for your Linux distribution (such as Ubuntu, Debian, or CentOS), then run:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install mariadb-server or
sudo yum install mariadb-server For step-by-step instructions, visit the official MariaDB installation guide.
2. Is MariaDB 12 faster than MySQL?
Yes. Benchmarks show that MariaDB 12 outperforms MySQL by up to 12% in common workloads, thanks to its enhanced optimizer, improved concurrency, and refined storage engine tuning. Performance gains are especially noticeable in analytical and write-heavy environments.
3. How do I upgrade safely to MariaDB 12?
Before upgrading, always back up your databases and test the migration in a staging environment. Use the MariaDB Upgrade Checker to detect deprecated variables and incompatible features. Then run the following command to adjust system tables and verify schema integrity:
sudo mariadb-upgrade 4. Where can I download MariaDB 12?
You can download the MariaDB 12.0 GA release directly from the official MariaDB download page. Packages are available for all major operating systems and architectures.
5. Can I use dbForge Studio with MariaDB 12?
Absolutely. dbForge Studio for MySQL provides full compatibility with MariaDB 12, allowing you to manage, develop, and optimize databases seamlessly in a modern graphical interface.
6. Can dbForge Studio optimize queries in MariaDB 12?
Yes. The Query Profiler and Execution Plan Viewer in dbForge Studio help you analyze and tune query performance for MariaDB 12. You can visually identify bottlenecks, compare query runs, and fine-tune SQL for faster execution.
7. Does dbForge Studio’s AI Assistant work with MariaDB 12 queries?
Yes. The AI Assistant understands MariaDB syntax and can generate, explain, or refactor SQL queries tailored to MariaDB 12. It’s an excellent companion for learning new syntax changes or optimizing complex statements.
8. Does dbForge Studio support schema compare for MariaDB 12?
Yes. The Schema and Data Compare tools in dbForge Studio let you quickly detect differences between MariaDB 12 databases or between versions, ensuring consistency during upgrades and deployments.

