NHibernate vs ADO.NET is the classic clash in .NET development: raw SQL muscle on one side, high-level abstraction on the other. One promises speed and precision, the other productivity and cleaner code.
For most .NET teams, the real challenge here is determining which approach best suits their project’s scale, timeline, and goals. That choice directly influences database efficiency, developer productivity, and long-term stability. And, while some teams commit fully to one approach, others find balance with a hybrid model: combining NHibernate with ADO.NET through the support of an ADO.NET provider.
In this guide, we’ll cut through the noise and compare NHibernate and ADO.NET. We will break down where each technology excels, where the trade-offs appear, and how you can align them with the needs of your .NET projects.
Table of contents- What is ADO.NET?
- What is NHibernate?
- Key differences between NHibernate and ADO.NET
- Performance comparison
- When to use NHibernate instead of ADO.NET
- When to use ADO.NET instead of NHibernate
- How dotConnect helps .NET developers with both approaches
- Conclusion
- FAQ
What is ADO.NET?
ADO.NET (ActiveX Data Objects for .NET) is the core framework for accessing relational data in the .NET ecosystem. Unlike object-relational mappers (ORMs) that abstract SQL, ADO.NET exposes database operations directly, giving developers complete control over queries, transactions, and connections. Its core components are as follows:
- SqlConnection: establishes and manages the connection to a database.
- SqlCommand: executes SQL statements or stored procedures with parameters.
- SqlDataReader: streams query results in a fast, forward-only, read-only manner.
- DataSet/DataTable with DataAdapter: provides a disconnected model, enabling data to be loaded into memory, modified offline, and synchronized back to the database.
Together, these tools form the building blocks for everything from simple queries to complex transactional workflows.

How ADO.NET works
ADO.NET follows a SQL-first approach: developers write raw queries or stored procedures, execute them through SqlCommand, and consume results using SqlDataReader or DataSet. This design puts query structure, transaction control, and connection management entirely in the developer’s hands. While it requires more boilerplate code, it minimizes runtime overhead and delivers predictable performance.
When to use ADO.NET
ADO.NET is most effective when projects demand tight control and maximum performance. Typical scenarios include:
- High-performance finance, trading, and analytics where ORM overhead isn’t acceptable.
- Custom SQL environments using stored procedures and database-specific features.
- Data-intensive tasks, such as ETL, bulk inserts, and large migrations.
- Lightweight utilities where direct SQL is faster than an ORM.
Because it minimizes abstraction, ADO.NET remains a trusted choice for enterprise applications where speed and precision are non-negotiable.
What is NHibernate?
NHibernate is a mature and widely adopted object-relational mapper (ORM) for .NET that helps developers bridge the gap between object-oriented domain models and relational databases. Instead of writing raw SQL, you interact with entities in C#, and NHibernate translates those operations into SQL behind the scenes. The key features of NHibernate are as follows:
- Lazy loading: loads related data only when accessed.
- Second-level caching: reduces queries by storing results in memory.
- Unit of work: commits multiple entity changes in one transaction.
- LINQ support: enables database queries with C# LINQ.
- Cross-database support: runs on different databases without query changes.
How NHibernate works
With NHibernate, developers define mappings in XML or Fluent configuration to link classes and properties to database tables and columns. When the application runs, NHibernate uses these mappings to generate SQL from object operations or LINQ/HQL queries, execute the commands, and return the results as fully populated .NET objects. Built-in features like lazy loading and caching simplify this process, cutting repetitive SQL and keeping the focus on domain logic rather than database plumbing.
When to use NHibernate
NHibernate is particularly valuable in projects where:
- Applications follow domain-driven design (DDD) and involve complex domain models.
- Long-term maintainability is critical, and SQL overhead is a burden.
- Teams need database independence for deployment or migration.
- Productivity outweighs raw control, with caching and mapping speeding delivery.
In short, NHibernate is the go-to choice when productivity, abstraction, and long-term maintainability matter more than raw SQL control.
With the basics covered, let’s compare NHibernate and ADO.NET to see what truly distinguishes them.
Key differences between NHibernate and ADO.NET
Although both ADO.NET and NHibernate are used for data access in .NET, they take very different approaches. The following table shows the difference between NHibernate and ADO.NET.
Comparison table
| Feature | ADO.NET | NHibernate |
|---|---|---|
| Querying | Manual SQL queries via SqlCommand or DataAdapter; complete control over SQL syntax. | LINQ or HQL queries are automatically translated to SQL through mapping. |
| Performance | High performance due to minimal abstraction and direct database access. | Slightly slower due to abstraction, yet can be optimized with caching and query tuning. |
| Learning curve | Easy for SQL-savvy developers; no need to learn ORM concepts. | Steeper learning curve with ORM patterns, mappings, and configuration. |
| Flexibility | Maximum flexibility — full control of SQL, schema, and transaction handling. | Less flexible at the SQL level; more stringent with object-relational mapping. |
| Maintainability | More boilerplate code; schema changes require manual updates and query adjustments. | Easier to maintain once mappings are set; reduces repeated queries and schema handling. |
| Tooling & ecosystem | Fully integrated into .NET; works across all relational databases. | Mature ORM ecosystem with LINQ, caching, lazy loading, XML, and fluent mapping options. |
| Use cases | Best for low-level operations, bulk inserts, and performance-critical tasks. | Best for domain-driven design, CRUD-heavy business apps, and rapid development cycles. |
| Best for | Developers needing raw SQL access, maximum performance, and custom workflows. | Teams building complex business applications where abstraction and maintainability matter more. |
This overview of NHibernate and ADO.NET differences reveals that ADO.NET is better suited for performance-critical tasks, while NHibernate is more suitable for complex domains. Next, let’s explore how developers interact with data using ADO.NET or NHibernate.
Programming model
ADO.NET and NHibernate differ most clearly in how developers write queries and interact with data:
- ADO.NET: utilizes manual SQL execution with SqlCommand, providing complete control over the query text, parameters, and transaction scope.
- NHibernate: uses an object-oriented approach with LINQ or HQL, where queries are written against entities and automatically translated into SQL.
Code examples
The following snippets highlight the divide: ADO.NET requires explicit SQL, NHibernate abstracts it into object queries.
ADO.NET
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
conn.Open();
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE Country = @country", conn);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@country", "USA");
SqlDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader();
while (reader.Read())
{
Console.WriteLine(reader["Name"]);
}
} This snippet opens a SQL connection, creates a parameterized query, executes it, and streams the results row by row with SqlDataReader. The developer writes and controls every part of the SQL and execution flow.
NHibernate
using (var session = sessionFactory.OpenSession())
{
var customers = session.Query<Customer>()
.Where(c => c.Country == "USA")
.ToList();
foreach (var customer in customers)
{
Console.WriteLine(customer.Name);
}
} Here, a session is opened, and the query is written in LINQ against the Customer entity. NHibernate translates it into SQL, executes it, and returns fully populated Customer objects. The developer works with entities, while SQL translation and execution are handled automatically.
Learning curve and complexity
Each technology requires a different level of expertise to use effectively:
- ADO.NET: easier to learn for SQL-savvy developers, since it requires no ORM concepts. Setup is fast, but large projects may accumulate boilerplate code.
- NHibernate: steeper learning curve with ORM patterns, mappings, and configuration. Once configured, however, it simplifies development and reduces repetitive SQL.
Community support and documentation also differ: ADO.NET is fully integrated into .NET and widely documented, whereas NHibernate has a smaller but mature community with extensive best practices.
Customization and flexibility
The trade-off between ADO.NET vs NHibernate comes down to control versus productivity:
- ADO.NET: allows complete SQL control, database-specific optimizations, and fine-grained transaction management. Ideal when you need predictable query behavior or vendor-specific features.
- NHibernate: prioritizes model-based development, hiding SQL complexity behind mappings and abstractions. Productivity improves, but flexibility at the SQL level is reduced.
Put simply, ADO.NET offers maximum control, while NHibernate enhances development at the cost of some flexibility.
Performance comparison
This section offers a NHibernate vs ADO.NET performance comparison. We show how each approach behaves under typical workloads.
| Aspect | ADO.NET | NHibernate |
|---|---|---|
| Overhead | Executes queries directly with no translation or materialization layer. | Executes queries with added translation, metadata lookups, and object materialization. |
| Execution control | Developers have complete control over SQL, indexing, and transactions. | Abstracts SQL behind mappings, reducing fine-grained control. |
| Workload fit | Excels in bulk inserts, batch processing, and analytics pipelines. | Fits CRUD-heavy apps and domain-driven models that benefit from abstraction and caching. |
| Performance tuning | Speed depends on developer-optimized SQL; minimal abstraction ensures consistent performance. | Provides caching, batching, and fetching strategies to reduce database hits and N+1 issues. |
| Benchmarks | Consistently faster than ORMs; e.g., retrieving 75k rows took ~867 ms in ADO.NET vs ~2,535 ms in NHibernate (~3× slower). Other tests confirm that fewer abstraction layers mean faster execution. | Misconfigured caching can negatively impact performance, but well-tuned strategies enable NHibernate to approach parity in read-heavy workloads. |
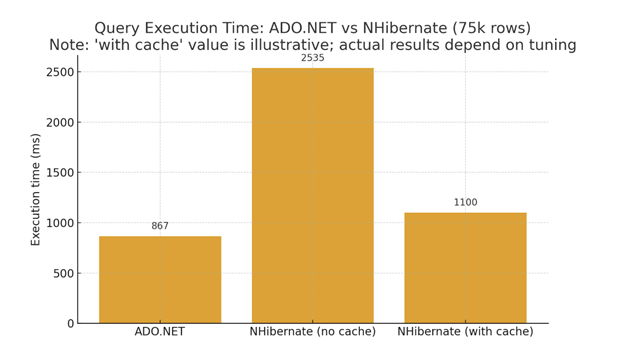
Summary:
- ADO.NET executes queries more efficiently due to its minimal overhead.
- NHibernate narrows the gap with caching but still carries translation costs.
Scenario-based performance comparison
The following NHibernate vs ADO.NET comparison highlights how each performs under various conditions.
| Scenario | Likely winner | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Simple, read-mostly queries | NHibernate (if cache effective) / ADO.NET | If the second-level cache is warmed and query patterns are stable, NHibernate can approach performance parity. |
| Bulk insert / massive writes | ADO.NET | Bypassing ORM overhead is almost always faster and more controllable. |
| Highly concurrent reads | NHibernate (with caching) / ADO.NET | If caching is used judiciously, NHibernate can reduce DB load, but ADO.NET scales better when caching is ineffective. |
| Variable, dynamic queries | ADO.NET | When queries change frequently (e.g., ad hoc reporting, flexible filtering), ORM overhead may become dominant. |
| Rapid development & moderate load | NHibernate | The productivity and maintainability wins outweigh the modest runtime cost. |
Takeaways:
- Use ADO.NET when performance, predictability, and SQL control are critical.
- Choose NHibernate when productivity and maintainability matter more than speed.
- Many enterprises adopt a hybrid approach, using NHibernate for business logic and ADO.NET for high-volume operations.
When to use NHibernate instead of ADO.NET
NHibernate is the stronger choice when applications emphasize abstraction and maintainability over direct SQL control. It is especially effective in scenarios such as:
- Fitting domain-driven design with complex models and rich business rules.
- Supporting long-term projects by reducing boilerplate and easing schema evolution.
- Providing database flexibility for migrations or multi-database deployments.
- Accelerating CRUD-heavy apps with caching, lazy loading, and LINQ for rapid development.
- Enabling testable architectures where persistence can be mocked or abstracted.
NHibernate delivers the most value when treated as a domain modeling tool, supporting scalability, abstraction, and long-term maintainability across complex applications.
When to use ADO.NET instead of NHibernate
ADO.NET stands out in scenarios where raw speed, memory efficiency, and direct SQL control are non-negotiable. It is especially effective for:
- Data import and export tools that demand high-throughput bulk operations.
- Real-time analytics dashboards where low-latency queries must be predictable.
- Batch processing and ETL pipelines handling large data volumes.
- Applications requiring strict memory control without ORM object overhead.
- Systems that rely on custom SQL or vendor-specific features such as query hints, window functions, or stored procedures.
As Microsoft Q&A emphasizes, ADO.NET is the foundation of .NET data access and consistently outperforms higher-level abstractions when performance and control are most important.
So, NHibernate or ADO.NET, which is better? Choose ADO.NET for high-load, SQL-driven applications, and NHibernate when abstraction and maintainability are a priority.
How dotConnect helps .NET developers with both approaches
dotConnect is a high-performance data provider built on top of ADO.NET that also integrates smoothly with ORMs like NHibernate. This dual capability makes it a practical choice for teams that need both raw SQL control and ORM abstraction within the same project.
dotConnect provides the following key benefits:
- Performance tuning: delivers optimized execution with connection pooling, batching, and fine-grained command control.
- NHibernate integration: works smoothly with NHibernate mappings and caching, allowing developers to utilize ORM features without compromising stability or vendor support.
- Direct SQL access: retains full compatibility with standard ADO.NET components (SqlConnection, SqlCommand, SqlDataReader), providing developers with maximum flexibility.
- Visual Studio integration: provides wizards, templates, and design-time tools to speed up development and simplify configuration.
- Flexible licensing: offers editions for small teams up to enterprise workloads, including perpetual options.
By supporting both NHibernate and ADO.NET workflows, dotConnect enables developers to choose the right tool for each part of an application without being locked into one approach.
Try dotConnect free and simplify your .NET data access strategy today!
Conclusion
An ADO.NET and NHibernate comparison is less about which is “better” and more about what your project demands. And since most applications need both raw performance and long-term maintainability, the most effective strategy is often to blend them: ADO.NET for high-load, SQL-heavy operations, and NHibernate for domain-driven business logic.
This is where dotConnect makes a difference. Instead of forcing teams to commit to one path, it supports both, giving you the raw performance of ADO.NET alongside the abstraction of NHibernate. With one toolset, you can design for today’s priorities while keeping the flexibility to adapt as your application grows.
Download dotConnect and see how it can enhance your .NET data access strategy.
FAQ
Is NHibernate still used?
Yes. While newer ORMs like Entity Framework Core have gained traction, NHibernate remains widely used in enterprise projects that follow domain-driven design or require advanced ORM features such as caching, batching, and custom mappings.
Is NHibernate or ADO.NET better for large-scale enterprise applications?
It depends on the workload. ADO.NET offers maximum performance and control, making it ideal for high-load or data-intensive systems. NHibernate is better suited for large applications with complex domain models, where abstraction and maintainability are critical.
What type of applications benefit most from using NHibernate instead of ADO.NET?
Applications with rich domain logic, long-term maintainability requirements, or teams that value rapid feature delivery benefit most from NHibernate. Its automated mapping and caching features reduce boilerplate code instances and speed up development.
Can NHibernate completely replace ADO.NET in modern .NET development?
No. NHibernate is built on top of ADO.NET, so ADO.NET remains the underlying data access layer. Developers who require direct control over raw SQL, custom queries, or bulk operations still rely on ADO.NET.
Is dotConnect compatible with both raw ADO.NET operations and NHibernate ORM?
Yes. dotConnect acts as a powerful ADO.NET provider while also offering integrations with ORMs like NHibernate. This allows teams to use both models in the same project without needing to switch tools.
How does dotConnect support both NHibernate and ADO.NET in a single .NET project?
dotConnect provides optimized database connectivity for ADO.NET and integrates seamlessly with NHibernate. Developers can run high-performance SQL operations alongside ORM-driven logic, all within the same solution.


