There are two types of IFs in MySQL: the IF statement and the IF function. Both are different from each other.
In this article, we will explain their diversities and show usage examples. Also, we will review other MySQL functions.
Contents
- MySQL IF statements: syntax and examples
- MySQL IF-THEN statement
- MySQL IF-THEN-ELSE statement
- MySQL IF-THEN-ELSEIF-ELSE statement
- Examples of MySQL IF statements
- MySQL IF function: definition and examples
- Conclusion
MySQL IF statements: syntax and examples
The IF statement allows you to verify a condition. There are three types of MySQL IF statements:
IF-THENIF-THEN-ELSEIF-THEN-ELSEIF-ELSE
MySQL IF-THEN statement
You can use IF-THEN to run a collection of SQL queries based on a condition. Here is the statement syntax:
IF condition THEN
statements;
END IF;If a specified condition evaluates to:
- true – statements between
IF-THENandEND-IFwill be executed - false – statements following the
END-IFblock will be applied
MySQL IF-THEN-ELSE statement
To execute statements when a condition in the IF block does not evaluate to true, you can use IF-THEN-ELSE. The syntax looks as follows:
IF condition THEN
statements;
ELSE
else-statements;
END IF;If a specified condition is:
- true – statements between
IF-THENandELSEwill be executed - false – statements following the
ELSEandEND-IFwill be executed
MySQL IF-THEN-ELSEIF-ELSE statement
Using IF-THEN-ELSEIF-ELSE, you can run statements based on several conditions. The syntax is given below:
IF condition THEN
statements;
ELSEIF elseif-condition THEN
elseif-statements;
...
ELSE
else-statements;
END IF;Let’s review each block. If a condition in IF-THEN is:
- true – statements will be executed
- false – elseif-condition will be evaluated
If elseif-condition in ELSEIF-THEN is:
- true – elseif-statements will be executed
- false – the next elseif-condition will be evaluated
And if there is no true condition both in the IF-THEN and in the ELSEIF-THEN blocks, else-statements will be applied.
Examples of MySQL IF statements
In this section, we are going to review examples of the IF statements usage. These examples involve calling MySQL stored procedures with parameters.
Need to install a MySQL database to follow our tutorial and check the examples first-hand? Explore the list of MySQL sample databases to practice SQL queries.
In the statement below, we declare the following condition using IF-THEN: if the sum of all empty entries in the STATUS column is more than 0, then in the output you will see the message “We have rows with NULL!!!”
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE GetEmtyStatus(
OUT Message VARCHAR(100))
BEGIN
DECLARE sum_null DECIMAL(10,2) DEFAULT 0;
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO sum_null FROM TASKS WHERE status IS NULL;
IF sum_null > 0 THEN
SET Message = 'We have rows with NULL!!!';
END IF;
END$$
DELIMITER ;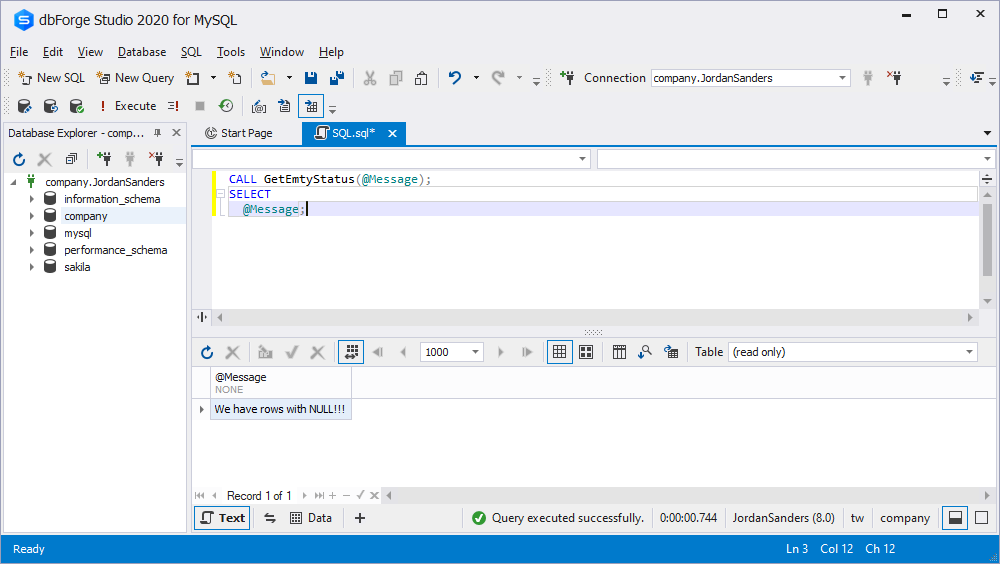
In this IF-THEN-ELSE statement, we specify two conditions:
- If the sum of all completed records in the STATUS column is 0, there will be the message “We have rows with NULL!!!”
- If the sum of all completed records in the STATUS column isn’t 0, you will see “We do not have rows with NULL!!!” in the output
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE GetEmptyStatusNotNull(
OUT Message VARCHAR(100))
BEGIN
DECLARE sum_null DECIMAL(10,2) DEFAULT 0;
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO sum_null FROM TASKS WHERE STATUS IS NOT NULL;
IF sum_null = 0 THEN
SET Message = 'We have rows with NULL!!!';
ELSE
SET Message = 'We do not have rows with NULL!!!' ;
END IF;
END$$
DELIMITER ;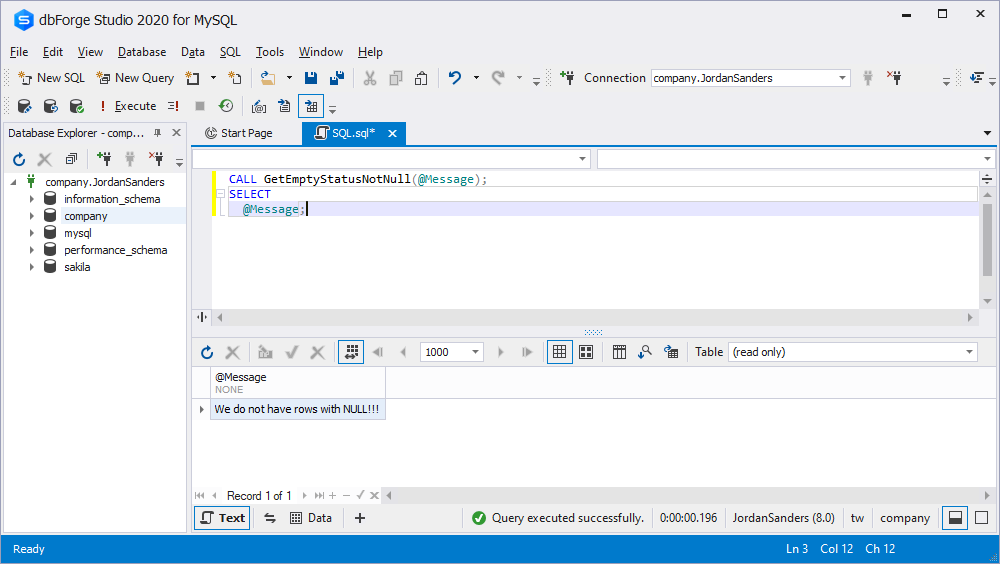
Using the IF-THEN-ELSEIF-ELSE statement, we set multiple conditions:
- If the sum of all empty values in the STATUS column is less than 3, the message “We have rows with NULL!!!” will be displayed
- If the sum of all empty values in the STATUS column is more than 3, you will see “We have NULL, but result is valid!!!”
- If the value does not satisfy two previous conditions, there will the message “We do not have rows with NULL!!!” in the output
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE CheckStatus(
OUT Message VARCHAR(100))
BEGIN
DECLARE sum_null DECIMAL(10,2) DEFAULT 0;
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO sum_null FROM TASKS WHERE STATUS IS NULL;
IF sum_null < 3 THEN
SET Message = 'We have rows with NULL!!!';
ELSEIF sum_null>3 THEN
SET Message = 'We have NULL, but result is valid!!!';
ELSE
SET Message = 'We do not have rows with NULL!!!' ;
END IF;
END$$
DELIMITER ;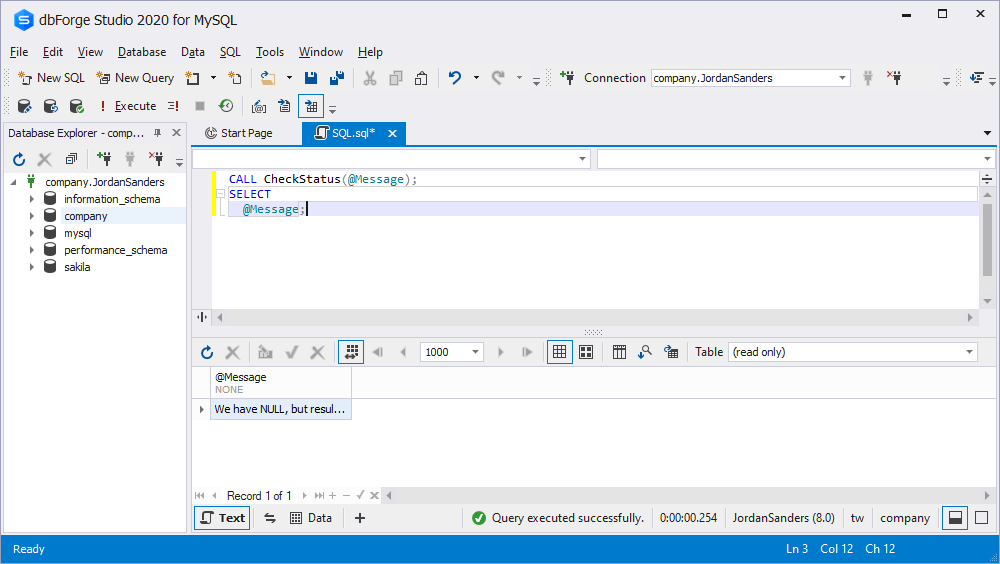
MySQL IF function: definition and examples
What is MySQL function?
Function in MySQL comprises a set of SQL statements with certain parameters that perform a task or operation and return a value as a result.
For example, the MySQL Version() function returns the current version of the MySQL database.
IF function vs IF statements
Pay attention that the IF function is not the same as the IF statement.
The IF function returns a value for a specified condition and has the following syntax:
IF(expr,if_true_expr,if_false_expr)The function returns if_true_expr if expr evaluates to true (it is not NULL). Otherwise, it returns if_false_expr. Based on how it is used, the IF function returns either a numeric value or a string.
Examples of MySQL IF function
Let’s review some examples of the IF function.
Example 1: MySQL IF function with aggregate functions
Aggregate functions calculate multiple values and provide a single value as a result. Using the IF function with aggregate functions can be beneficial to retrieve a specific output.
In this section, we’ll review some aggregate functions that can be used with the IF function.
MySQL SUM IF
For example, if you want to know how many job tasks you have completed or still planned this month, you can use the function with the SUM aggregate function, as in the following query:
SELECT
SUM(IF(status = 'Completed', 1, 0)) AS Completed
FROM
tasks;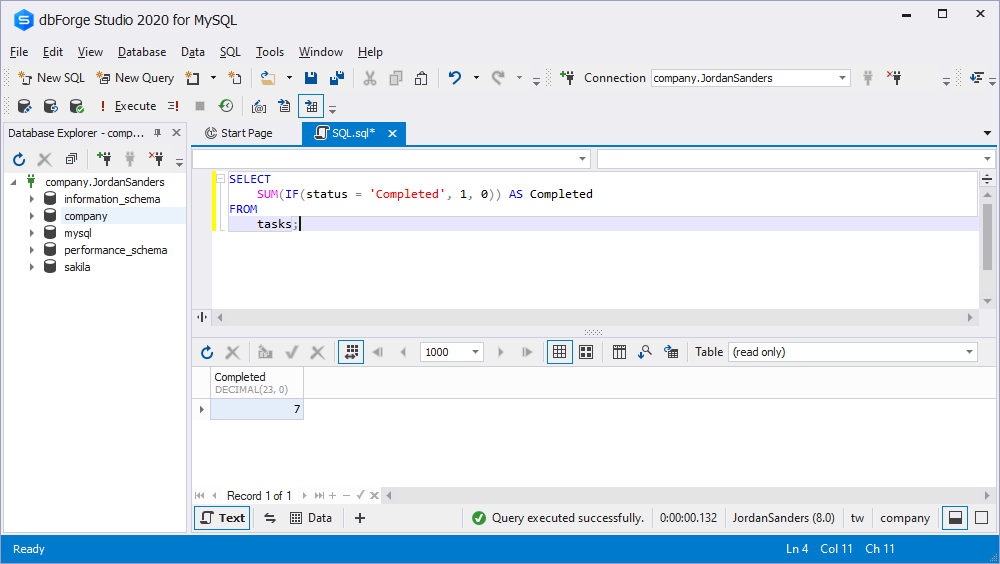
In the query above, if the task status is completed or planned, the IF function returns 1 or 0. The SUM function determines the total number of planned and completed tasks depending on the returned value of the IF function.
MySQL COUNT IF
It is possible to combine the IF function with MySQL COUNT function. We choose the task’s status in the Tasks table using the following query:
SELECT DISTINCT
status
FROM
orders
ORDER BY status;
SELECT DISTINCT
status
FROM
tasks
ORDER BY status;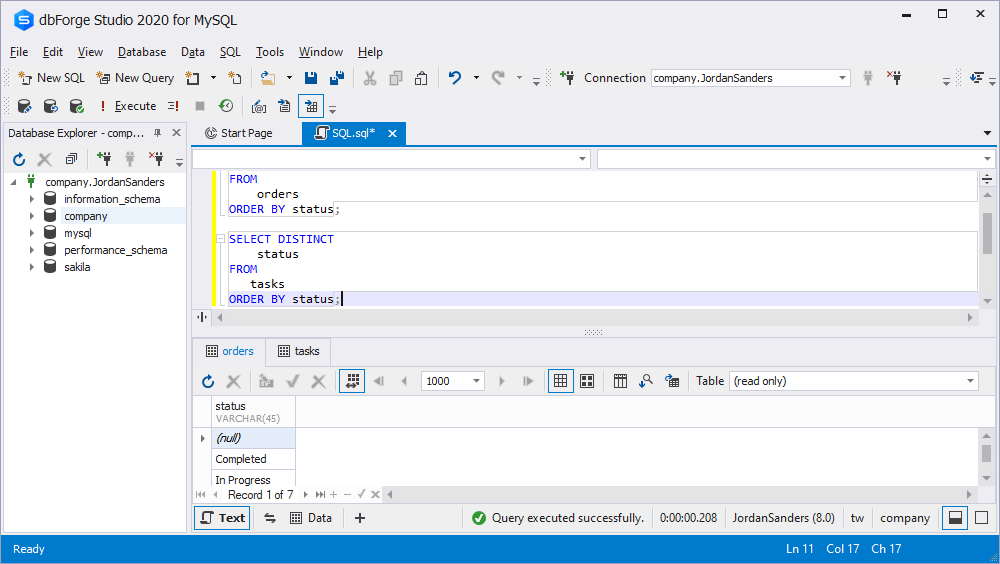
By combining the IF function with COUNT, we can find out how many tasks are in each status at any given time. As NULL values are not counted by the COUNT function, the IF function returns NULL if the status is not in the selected status, and 1 otherwise. Take a look at the following query:
SELECT
COUNT(IF(status = 'Completed', 1, NULL)) Completed,
COUNT(IF(status = 'Reopened', 1, NULL)) Reopened,
COUNT(IF(status = 'In Progress', 1, NULL)) 'In Progress',
COUNT(IF(status = 'In Review', 1, NULL)) 'In Review',
COUNT(IF(status = 'Planned', 1, NULL)) 'Planned'
FROM
tasks;You can also get a similar result without the IF function by using the GROUP BY clause and the COUNT function, as shown below:
SELECT status, COUNT(STATUS)
FROM tasks
GROUP BY status;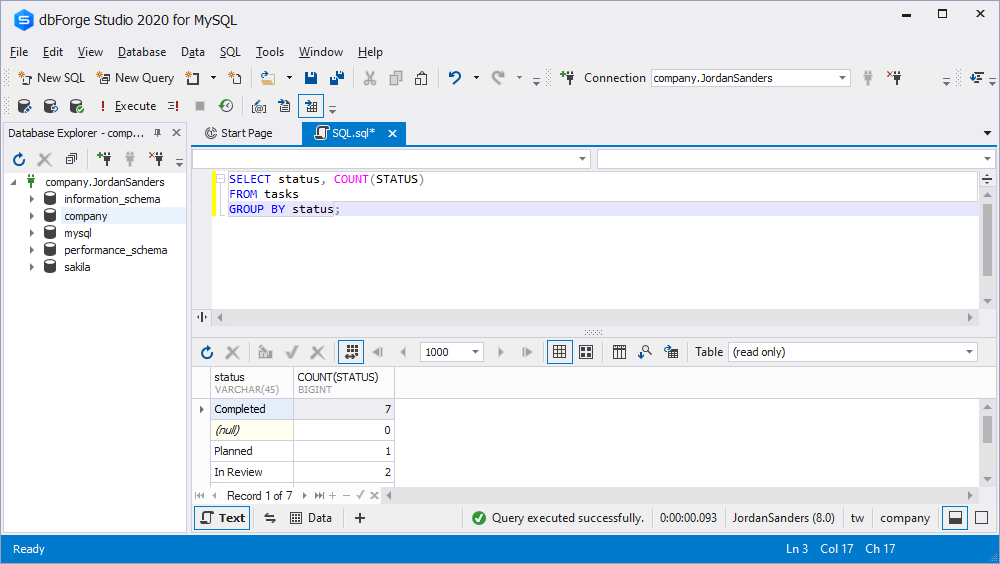
Example 2: the NULLIF function
MySQL NULLIF is used to compare two expressions:
NULLIF(expr1, expr2)The function returns NULL if both expressions are equal, otherwise, it returns the first expression. Let’s try it in practice:
SELECT NULLIF(25, 25);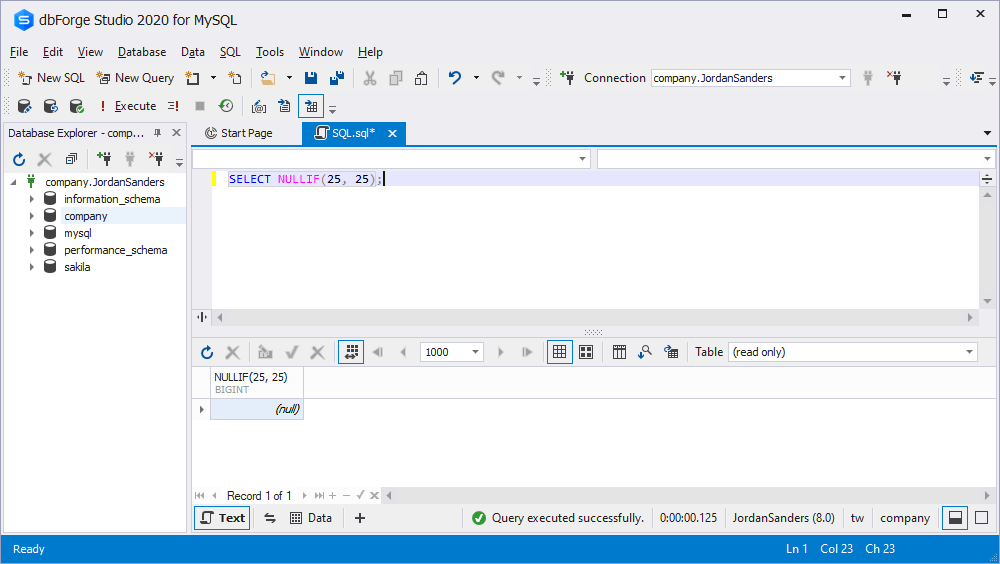
As you can see, both expressions are equal, that is why the function returned NULL.
Example 3: the IFNULL function
MySQL IFNULL is used to check for any NULL values in specified expressions:
IFNULL(expr_1, expr_2)The function returns expr_1 if the expression is NOT NULL. Otherwise, it returns expr_2 if the expression is NULL. So, for example, if you run:
SELECT IFNULL(NULL, 500);You will get such an output:
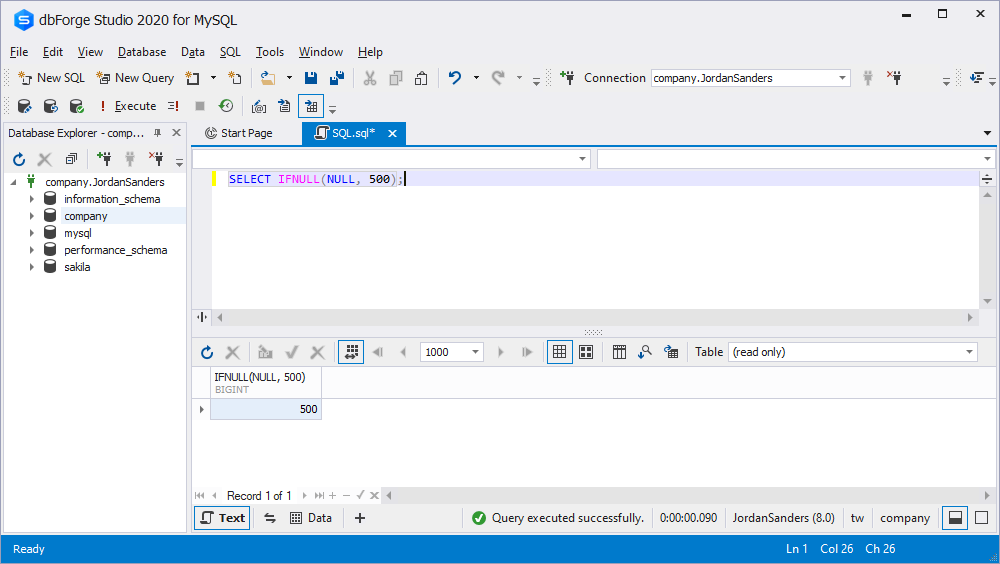
The function returned 500 because the expression in NULL.
Example 4: display N/A instead of NULL using MySQL IF function
Let’s create a demo MySQL table Company. Many employees in the Employees table have no data in the city column, and as a result, when we select employees, the city column shows NULL values. Take a look at the following query:
SELECT
employeeNumber, employeeName, age, city
FROM
employees;To improve the output, we can use the IF function to return N/A if the city is NULL, as shown by the following query:
SELECT
employeeNumber,
employeeName,
IFNULL(city, 'N/A'),
age
FROM
employees;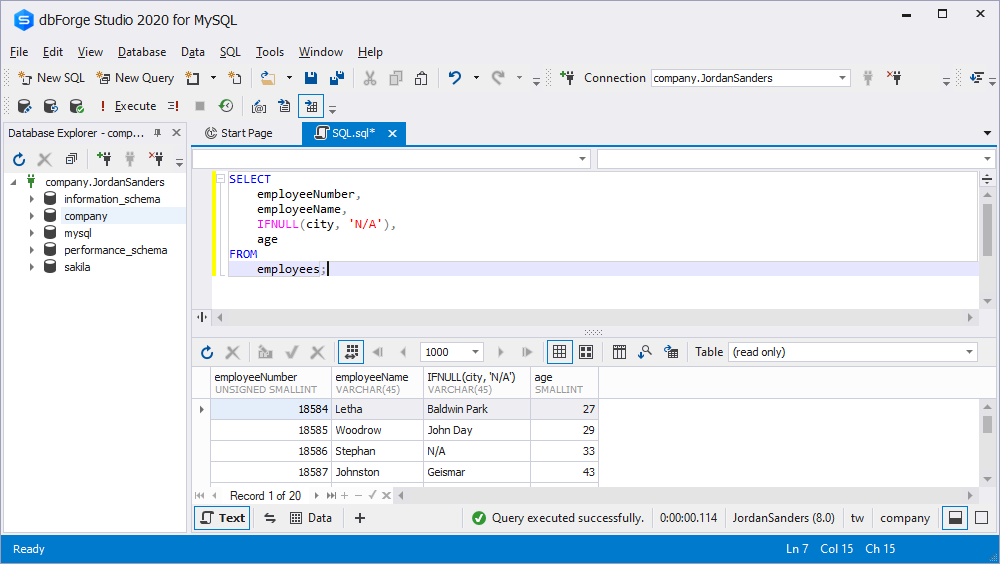
Curious how you can create pivot tables and highlight insights from MySQL databases without complex coding? Check MySQL Pivot Table option within dbForge Studio for MySQL.
Conclusion
In this article, we have found out the differences between MySQL IF statement and IF function and reviewed other MySQL functions. Also, we have shown a small part of the usage variations for both of them. Actually, there are a lot of MySQL statements, queries, and functions. That’s why, database administrators must have a reliable and easy-to-use tool to facilitate their routine work.
For example, dbForge Studio for MySQL can become your indispensable assistant for database development, management, and administration. As one of the most powerful MySQL database tools, it offers rich features like code completion, formatting, data reports, and more.
For example, dbForge Studio for MySQL can become your indispensable assistant for database development, management, and administration. As one of the most powerful MySQL database tools, it offers rich features among which you can find code completion and code formatting, data reports, and many more. By the way, with Query Builder delivered by dbForge Studio for MySQL, you can create queries of any complexity in the MySQL visual query editor.
For more information about dbForge Studio for MySQL, feel free to watch these video tutorials. Also, we have related posts about MySQL statements, and if you would like to read them, here they are:
- GROUP BY Statement in MySQL With Twelve Examples
- MySQL SELECT Statement Basics
- WHERE Condition in MySQL with 16 Different Query Examples
- MySQL INSERT Statement – Inserting Rows into a Table

